Introduction
The COVID-19 pandemic has brought to light the intricate interplay between viral infections and pre-existing health conditions, notably diabetes. As researchers delve deeper into understanding this relationship, it becomes increasingly evident that individuals with diabetes face heightened risks and challenges when confronted with the novel coronavirus. In this comprehensive guide, we explore the nuanced connection between COVID-19 and diabetes, shedding light on the underlying mechanisms, risk factors, and preventive measures to empower individuals and healthcare professionals alike. All You Need To Know About (arms And Legs Tingling)
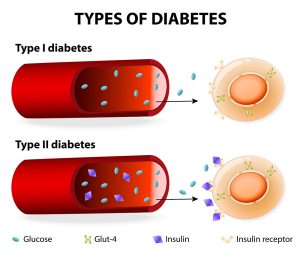
Understanding Diabetes
Before delving into the impact of COVID-19 on individuals with diabetes, it’s crucial to grasp the fundamentals of this chronic metabolic disorder. Diabetes mellitus encompasses a group of diseases characterized by elevated blood sugar levels resulting from either insufficient insulin production or the body’s inability to effectively utilize insulin. The two primary forms of diabetes are type 1 and type 2, each with distinct etiologies and management strategies.
Type 1 Diabetes: An Autoimmune Phenomenon
Type 1 diabetes, often diagnosed in childhood or adolescence, arises from autoimmune destruction of the pancreatic beta cells responsible for insulin secretion. This results in an absolute deficiency of insulin, necessitating lifelong insulin replacement therapy to regulate blood glucose levels.
Type 2 Diabetes: A Complex Interplay of Factors
Contrastingly, type 2 diabetes typically develops in adulthood and is characterized by insulin resistance, wherein the body’s cells become less responsive to insulin’s actions. Genetic predisposition, sedentary lifestyle, poor dietary habits, and obesity are among the primary contributors to type 2 diabetes, making it a multifactorial condition that demands comprehensive management strategies encompassing lifestyle modifications, pharmacotherapy, and, in some cases, insulin therapy.
Unraveling the Nexus of Risks
Why Diabetes Matters
Individuals with diabetes face an elevated risk of experiencing severe complications if infected with COVID-19. Several factors contribute to this heightened vulnerability, including impaired immune function, chronic inflammation, and comorbidities such as cardiovascular disease and hypertension, which frequently coexist with diabetes.
Impact on Glycemic Control
Moreover, the physiological stress induced by viral infections like COVID-19 can disrupt glycemic control in individuals with diabetes, leading to hyperglycemia or, in severe cases, diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA). The inflammatory response triggered by the virus, coupled with the use of certain medications such as glucocorticoids, further complicates glucose management and necessitates vigilant monitoring and adjustment of treatment regimens.
Compounding Complications
Compounding the challenges posed by COVID-19, individuals with diabetes are more prone to developing secondary complications, including respiratory distress syndrome, acute kidney injury, and cardiovascular complications. The intricate interplay between diabetes-related endothelial dysfunction, hypercoagulability, and systemic inflammation predisposes these individuals to a cascade of adverse outcomes, necessitating prompt intervention and multidisciplinary care.
Strategies for Optimal Management
A Proactive Approach
In the face of the COVID-19 pandemic, prevention emerges as the cornerstone of mitigating risks for individuals with diabetes. Adhering to strict infection control measures, including frequent hand hygiene, wearing masks, and practicing physical distancing, remains imperative to minimize the risk of viral transmission. Additionally, prioritizing annual influenza vaccination and, when available, COVID-19 vaccination can confer added protection against respiratory infections.
Empowering Self-Management
Empowering individuals with diabetes to actively manage their condition assumes heightened significance in the context of the pandemic. Educating patients about the importance of adhering to prescribed treatment regimens, monitoring blood glucose levels diligently, and recognizing early warning signs of deteriorating health equips them with the tools necessary to navigate the uncertainties posed by COVID-19 effectively.
Facilitating Remote Care
The advent of telemedicine has revolutionized healthcare delivery, offering a lifeline for individuals with diabetes amidst the constraints imposed by the pandemic. Teleconsultations enable healthcare providers to conduct routine follow-ups, monitor glycemic parameters, and provide timely guidance and support to patients from the safety and comfort of their homes, minimizing the risk of exposure to contagious pathogens.
Understanding the Impact
| Factors | COVID-19 | Diabetes |
|---|---|---|
| Immune Response | Heightened susceptibility to infection | Impaired immune function |
| Glycemic Control | Disruption leading to hyperglycemia | Challenges in maintaining blood sugar levels |
| Complications | Increased risk of severe outcomes | Elevated susceptibility to secondary issues |
| Management | Focus on infection control and treatment | Emphasis on lifestyle modifications and care |
Conclusion
In conclusion, the intricate interplay between COVID-19 and diabetes underscores the urgent need for tailored strategies aimed at mitigating risks, enhancing resilience, and safeguarding the health and well-being of individuals living with diabetes. By fostering collaboration between healthcare professionals, empowering patients through education and self-management, and leveraging innovative technologies such as telemedicine, we can navigate the challenges posed by the pandemic with resilience and resolve. Together, we can turn the tide against COVID-19 and ensure a brighter, healthier future for all.




