Gravitational physics, often considered one of the most fascinating branches of physics, deals with the study of gravity and its effects on the universe. From the gentle pull of a falling apple to the immense forces shaping galaxies, gravity is a fundamental force that governs the motion of celestial bodies and the structure of spacetime itself.
What is Gravitational Physics?
Gravitational physics is the field of physics concerned with the study of gravity, its effects, and its interactions with matter and energy. It seeks to understand the nature of gravity and its role in shaping the universe.
Importance of Understanding Gravity
Understanding gravity is crucial for comprehending the behavior of celestial objects, ranging from planets and stars to entire galaxies. It is also essential for various practical applications, such as space exploration and satellite navigation.
Historical Background
Isaac Newton and the Law of Universal Gravitation
In the 17th century, Sir Isaac Newton formulated the Law of Universal Gravitation, which states that every mass attracts every other mass with a force proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
Albert Einstein and General Relativity
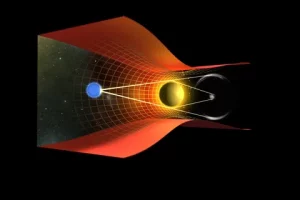
In the early 20th century, Albert Einstein revolutionized our understanding of gravity with his theory of General Relativity. According to General Relativity, gravity arises from the curvature of spacetime caused by the presence of mass and energy.
Key Concepts in Gravitational Physics
Mass and Gravity
Mass is a measure of the amount of matter in an object, while gravity is the force of attraction between masses. The greater the mass of an object, the stronger its gravitational pull.
Space-Time Curvature
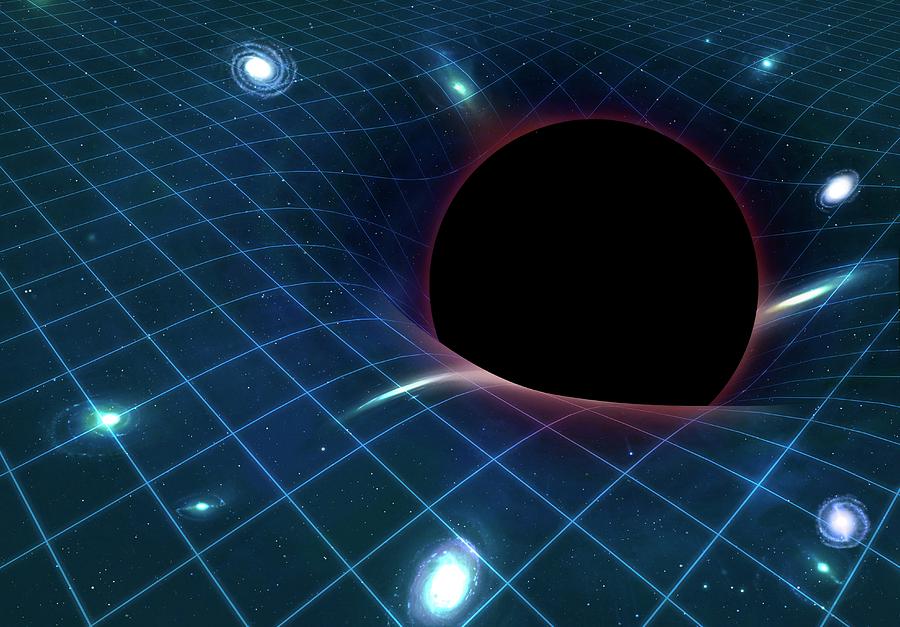
According to General Relativity, massive objects deform the fabric of spacetime, causing it to curve. This curvature is what we perceive as gravity, as objects follow the curved paths created by this distortion.
Black Holes and Singularities
Black holes are regions of spacetime where gravity is so strong that nothing, not even light, can escape its pull. At the center of a black hole lies a singularity, a point of infinite density where the laws of physics as we know them break down.
Gravitational Physics

Space Exploration
Gravitational physics plays a crucial role in space exploration, helping scientists understand the motion of celestial bodies and plan missions to distant planets and beyond.
Astrophysics
The study of gravitational physics is essential for astrophysics, allowing researchers to investigate phenomena such as the formation and evolution of stars, galaxies, and the universe itself.
Geophysics
On Earth, gravitational physics is used in geophysics to study the structure and composition of the planet, including its interior and gravitational anomalies.
Challenges and Current Research
Quantum Gravity
One of the biggest challenges in gravitational physics is reconciling General Relativity with quantum mechanics to develop a theory of quantum gravity that can describe the behavior of gravity at the smallest scales.
Dark Matter and Dark Energy
Gravitational physics also grapples with mysteries such as dark matter and dark energy, which together make up the majority of the universe’s mass-energy content but remain largely elusive and poorly understood.
Conclusion
Gravitational physics is a captivating field that delves into the mysteries of gravity and its profound influence on the cosmos. From the groundbreaking insights of Newton and Einstein to the cutting-edge research of today, our understanding of gravity continues to evolve, uncovering new wonders and challenges alike.
FAQs
1. What is the difference between Newtonian gravity and General Relativity?
Newtonian gravity describes gravity as a force acting at a distance between masses, while General Relativity views gravity as the curvature of spacetime caused by mass and energy.
2. How do black holes form?
Black holes form when massive stars collapse under their own gravity at the end of their life cycle, creating a region of spacetime where gravity is so strong that nothing can escape.
3. What is dark matter?
Dark matter is a mysterious form of matter that does not emit, absorb, or reflect light, yet exerts gravitational influence on visible matter. Its nature remains unknown.
4. Why is quantum gravity important?
Quantum gravity is essential for understanding the behavior of gravity at the smallest scales, such as those found in the early universe or near the singularity of a black hole.
5. How does gravitational physics impact everyday life?
Gravitational physics impacts everyday life through applications such as satellite navigation, telecommunications, and the design of spacecraft and buildings.