Author Intro
Dr. Amelia Patel, a renowned transplant surgeon with over 15 years of experience, dives into the recent pig kidney transplant case and its significance for the future of xenotransplantation, a field brimming with both hope and challenges.
Navigating the Landscape: Xenotransplantation Explained
Xenotransplantation, the transplantation of organs or tissues from one species to another, has emerged as a potential solution to the critical organ shortage. This procedure, particularly pig-to-human transplants, holds immense promise due to pigs’ anatomical similarities to humans.
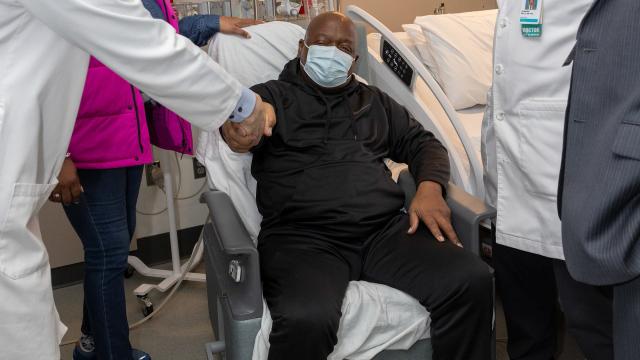
A Landmark Case: The First Pig Kidney Transplant
In a groundbreaking surgery, Richard Slayman, a patient with end-stage kidney disease, received a genetically modified pig kidney at Massachusetts General Hospital. While the transplant itself was successful, Mr. Slayman sadly passed away two months later.
Unveiling the Cause: Transparency is Key
The exact cause of Mr. Slayman’s death remains under investigation. However, this case highlights the importance of transparency in xenotransplantation research.
Informative Table: Key Points of the Pig Kidney Transplant Case
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Patient | Richard Slayman |
| Underlying Condition | End-stage kidney disease |
| Type of Transplant | Genetically modified pig kidney |
| Outcome | Transplant successful, patient died two months later |
| Cause of Death | Under investigation |
Beyond the Headlines: Addressing Challenges
While the pig kidney transplant marks a significant step forward, challenges remain:
- Immune Rejection: The human body’s natural defense system can aggressively reject foreign tissues. Continued research on immunosuppressive medications is crucial.
- Ethical Considerations: Concerns regarding animal welfare and potential transmission of animal diseases require careful consideration.
A Beacon of Hope: The Road Ahead
Despite the challenges, the pig kidney transplant paves the way for a future where xenotransplantation saves countless lives.
Comparative Table: Traditional Organ Transplants vs. Xenotransplantation
| Feature | Traditional Transplants | Xenotransplantation |
|---|---|---|
| Organ Source | Deceased human donors | Genetically modified animals |
| Waiting List Time | Extensive wait times | Potentially shorter wait times |
| Availability | Limited organ supply | Potentially abundant organ supply |
| Ethical Concerns | Focus on informed consent | Focus on animal welfare and disease transmission |
Conclusion: A Collaborative Effort
The field of xenotransplantation requires a collaborative effort from transplant surgeons, immunologists, ethicists, and regulatory bodies. Open communication and ongoing research hold the key to unlocking the full potential of this life-saving technology.