Introduction:
Cocaine, a potent stimulant notorious for its recreational use, has been consistently associated with adverse cardiovascular effects, including an increased risk of Heart Attack. This article provides a detailed exploration of the relationship between cocaine use and heart attacks, shedding light on symptoms, short-term and long-term effects, available treatments, and the crucial role of support in addressing addiction.
Can Cocaine Cause a Heart Attack?
- Mechanisms of Impact:
- Cocaine’s potent stimulant properties significantly affect the cardiovascular system.
- Elevates blood pressure and induces arrhythmia, creating a conducive environment for heart attacks.
- Statistical Insight:
- In 2021, nearly 25,000 deaths in the U.S. were directly linked to cocaine use.
- Primary causes included seizures and heart attacks, emphasizing the severity of the issue.

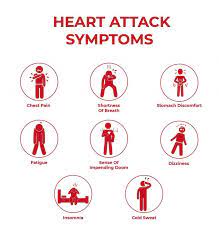
Symptoms of Cocaine-Induced Heart Attack:
- Distinctive Signs:
- Chest tightness, discomfort, and shortness of breath are common symptoms.
- Cocaine’s impact on capillaries restricts blood flow, exacerbating the strain on the heart.
- Urgency of Medical Attention:
- Prompt medical assistance is crucial when symptoms like dizziness, weakness, or jaw pain manifest.
- Cocaine-induced heart attacks are life-threatening and demand immediate intervention.
Effects of Cocaine on Heart Health:
- Beyond Heart Attacks:
- Cocaine use has multifaceted effects on heart health beyond inducing heart attacks.
- Increases blood pressure, contributes to coronary artery disease, induces arrhythmia, and may lead to congestive heart failure.
- Immediate vs. Long-term Effects:
- Short-term effects involve heightened energy, paranoia, and increased heart rate.
- Long-term consequences encompass significant health complications, including weight loss, gastrointestinal issues, stroke risk, and heart inflammation.
Cocaine-Induced Heart Attack Treatment:
- Parallel to Typical Heart Attack Care:
- Treatment parallels that of a typical heart attack, with some exceptions.
- Beta-blockers, crucial in typical cases, cannot be administered due to potential complications in cocaine-induced episodes.
- Utilization of Medications:
- Anticoagulant drugs, vasodilators, and nitroglycerin are employed to prevent clot formation, improve blood flow, and reverse vasoconstriction.
- Surgical interventions may be necessary to repair damaged heart valves or other cardiovascular components.

Support for Cocaine Use:
- Confidential Assistance:
- Organizations like SAMHSA provide confidential helplines for individuals dealing with substance use disorders and mental illnesses.
- Cocaine Anonymous offers support through shared experiences, strength, and hope for those battling cocaine addiction.
- Holistic Rehabilitation:
- Seeking medical assistance for rehabilitation is crucial, addressing withdrawal symptoms and providing a structured approach to quitting drugs.
- Lifestyle modifications, including quitting smoking and controlling conditions like diabetes and hypertension, play a pivotal role in long-term recovery.
Summary:
Understanding the intricate interplay between cocaine use and heart attacks is paramount for individuals and healthcare professionals alike. The immediate and long-term consequences underscore the need for comprehensive approaches to treatment, including medical interventions, support from organizations, and lifestyle modifications. By unraveling the complexities of this relationship, we aim to contribute to a greater awareness of the challenges posed by cocaine use and foster a proactive approach to mitigating its impact on heart health.




