Introduction
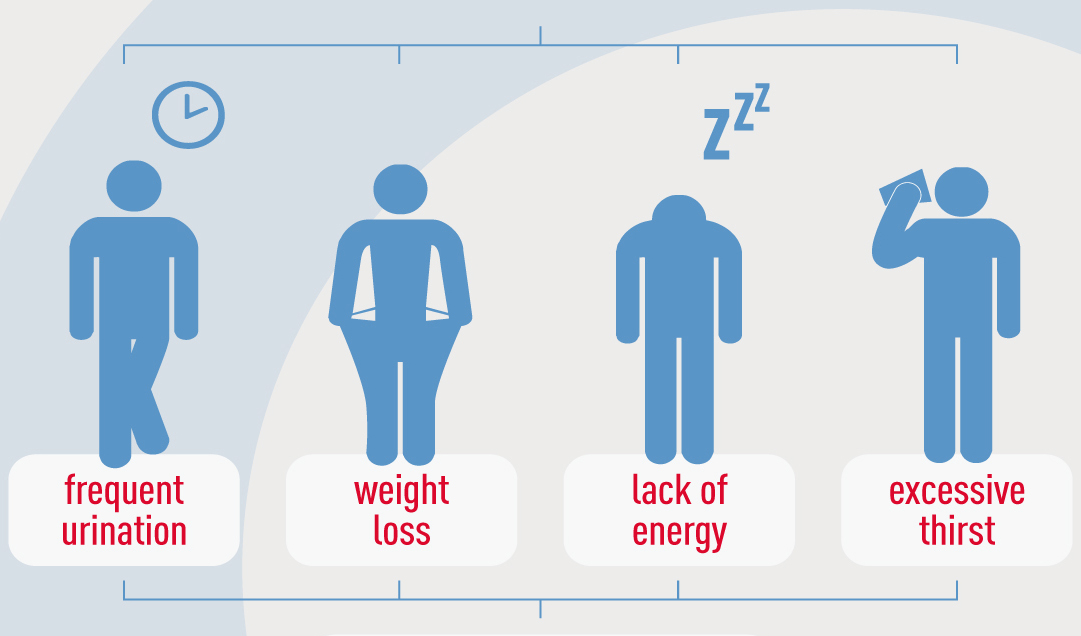
The journey to understanding and managing Type 2 diabetes begins with a diagnosis. But how is it accurately determined? In this article, we will peel back the layers of the diagnostic process, including the crucial blood tests like HbA1c and fasting blood sugar levels. Moreover, we will explore the indispensable role of medical professionals in confirming a Type 2 diabetes diagnosis.
The Diagnostic Process Unveiled
Diagnosing Type 2 diabetes involves a systematic process that typically includes the following steps:
- Medical History: Your healthcare provider will begin by taking a detailed medical history, asking about your symptoms, risk factors, and family history of diabetes. This information provides essential context for the diagnosis.
- Physical Examination: A physical examination can reveal signs of diabetes, such as weight loss, high blood pressure, or skin changes.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests are the cornerstone of diagnosing Type 2 diabetes. Two key tests are often used:
- Fasting Blood Sugar Level: This test measures your blood sugar level after an overnight fast. A fasting blood sugar level of 126 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) or higher on two separate occasions indicates diabetes.
- HbA1c Test: The HbA1c test, also known as the hemoglobin A1c test, provides an average of your blood sugar levels over the past two to three months. An HbA1c level of 6.5% or higher is indicative of diabetes.
https://th.bing.com/th/id/R.99dd0bbe14184ecd03004dde86e818eb?rik=kKZkbDRukyZ3kA&riu=http%3a%2f%2fwww.healthgoesup.com%2fwp-content%2fuploads%2f2017%2f06%2f2diabetes-symptoms.jpg&ehk=7y3%2babqwf8ZQfftAfXI%2brwsnSgsaL3QXmkdn6QM2zTM%3d&risl=&pid=ImgRaw&r=0
The Role of Medical Professionals
The diagnostic process for Type 2 diabetes involves several healthcare professionals, each playing a crucial role:
- General Practitioners: General practitioners (GPs) are often the first point of contact for individuals concerned about diabetes. They conduct initial assessments, order blood tests, and provide guidance on lifestyle changes.
- Endocrinologists: Endocrinologists are specialists in hormonal disorders, including diabetes. If a diagnosis is confirmed, endocrinologists may become involved to provide more specialized care and treatment.
- Diabetes Educators: Diabetes educators are instrumental in educating individuals on managing their condition. They offer guidance on diet, exercise, blood sugar monitoring, and medication management.
- Dietitians: Dietitians help individuals with diabetes create balanced meal plans to manage blood sugar levels and maintain overall health.
Confirming the Diagnosis
It’s important to note that a single elevated blood test result is not always sufficient to confirm a Type 2 diabetes diagnosis. To confirm the diagnosis, healthcare professionals often use the same test for a second time or may conduct additional tests.
The Importance of Early Diagnosis
Diagnosing Type 2 diabetes in its early stages is critical for effective management and reducing the risk of complications. Prompt diagnosis allows individuals to begin appropriate treatment, make lifestyle changes, and closely monitor their blood sugar levels.

Conclusion
The diagnostic process for Type 2 diabetes is a well-structured journey that involves medical professionals, comprehensive blood tests, and a thorough assessment of an individual’s medical history and risk factors. Accurate diagnosis is the first step toward effective management, empowering individuals to take control of their health and make informed decisions about their treatment and lifestyle. If you suspect you may have diabetes, seeking the guidance of a healthcare professional is your pathway to understanding and managing this condition.