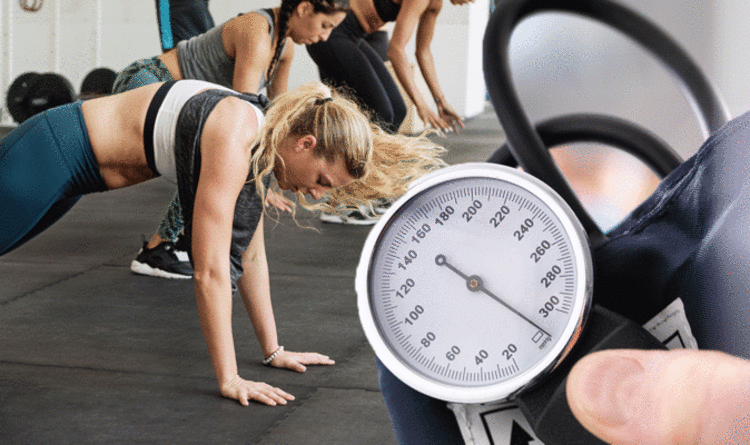Understanding Blood Pressure
Blood pressure is the force of blood pushing against the walls of arteries as it flows through the body. It’s vital for delivering oxygen and nutrients to organs and tissues. Blood pressure is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg), with two numbers: systolic (when the heart beats) and diastolic (when the heart is at rest). A normal reading is around 120/80 mmHg.
The Importance of Healthy Blood Pressure
Maintaining healthy blood pressure is crucial for overall well-being. High blood pressure (hypertension) can lead to heart disease, stroke, and kidney problems, while low blood pressure (hypotension) can cause dizziness and fainting.
Exercise and Its Impact on Blood Pressure
Regular exercise is key to lowering blood pressure and reducing the risk of hypertension. Here’s how it works:
Aerobic Exercise
Aerobic exercise like walking, jogging, or swimming strengthens the heart, improves circulation, and lowers blood pressure over time.
Strength Training
Strength training builds muscle mass, which boosts metabolism and supports weight management, indirectly aiding blood pressure regulation.
Flexibility and Balance Exercises
Flexibility and balance exercises such as yoga promote relaxation and stress reduction, contributing to better cardiovascular health.

Mechanism Behind Exercise and Blood Pressure Reduction
Several factors contribute to exercise’s blood pressure-lowering effect:
Improved Blood Vessel Function
Exercise enhances the health of blood vessels, promoting vasodilation and reducing resistance to blood flow.
Reduced Sympathetic Nervous System Activity
Regular exercise decreases activity in the sympathetic nervous system, which controls heart rate and blood vessel constriction.
Lowered Inflammatory Markers
Exercise reduces inflammation, protecting blood vessels and maintaining healthy blood pressure levels.
Weight Management
By burning calories and promoting fat loss, exercise helps maintain a healthy weight, reducing the risk of hypertension. explore more About ( white spots on nails )

Designing an Exercise Program for Blood Pressure Management
Here’s how to create an exercise program for managing blood pressure:
Consultation with Healthcare Provider
Consult a healthcare provider before starting any exercise regimen, especially if you have hypertension or other cardiovascular conditions.
Gradual Progression
Start slowly and gradually increase the intensity and duration of exercise sessions to avoid injury.
Variety of Activities
Incorporate a variety of exercises to maximize benefits and prevent boredom.
Consistency is Key
Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity per week for optimal results.
Monitoring Progress
Regularly monitor blood pressure levels to track progress and adjust the exercise routine as needed.
Effects of Different Types of Exercise on Blood Pressure
| Exercise Type | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Aerobic Exercise | Strengthens heart, improves circulation |
| Strength Training | Builds muscle mass, aids weight management |
| Flexibility Exercise | Promotes relaxation, reduces stress |
Conclusion
Exercise is a powerful tool for managing blood pressure and improving overall cardiovascular health. By incorporating regular physical activity into your routine and following a well-designed exercise program, you can lower your blood pressure, reduce the risk of hypertension, and enhance your quality of life.