Cancer remains one of the most formidable challenges in modern medicine, with millions of new cases diagnosed each year. Traditional treatments, such as chemotherapy and radiation, have made significant strides in increasing survival rates. However, these methods often come with severe side effects and are not universally effective. The advent of personalized cancer treatments marks a revolutionary shift in oncology, promising more effective and less harmful therapeutic options. This article delves into the current landscape and future prospects of personalized cancer treatments, focusing on key areas such as genomics, immunotherapy, and artificial intelligence (AI).
The Genomic Revolution
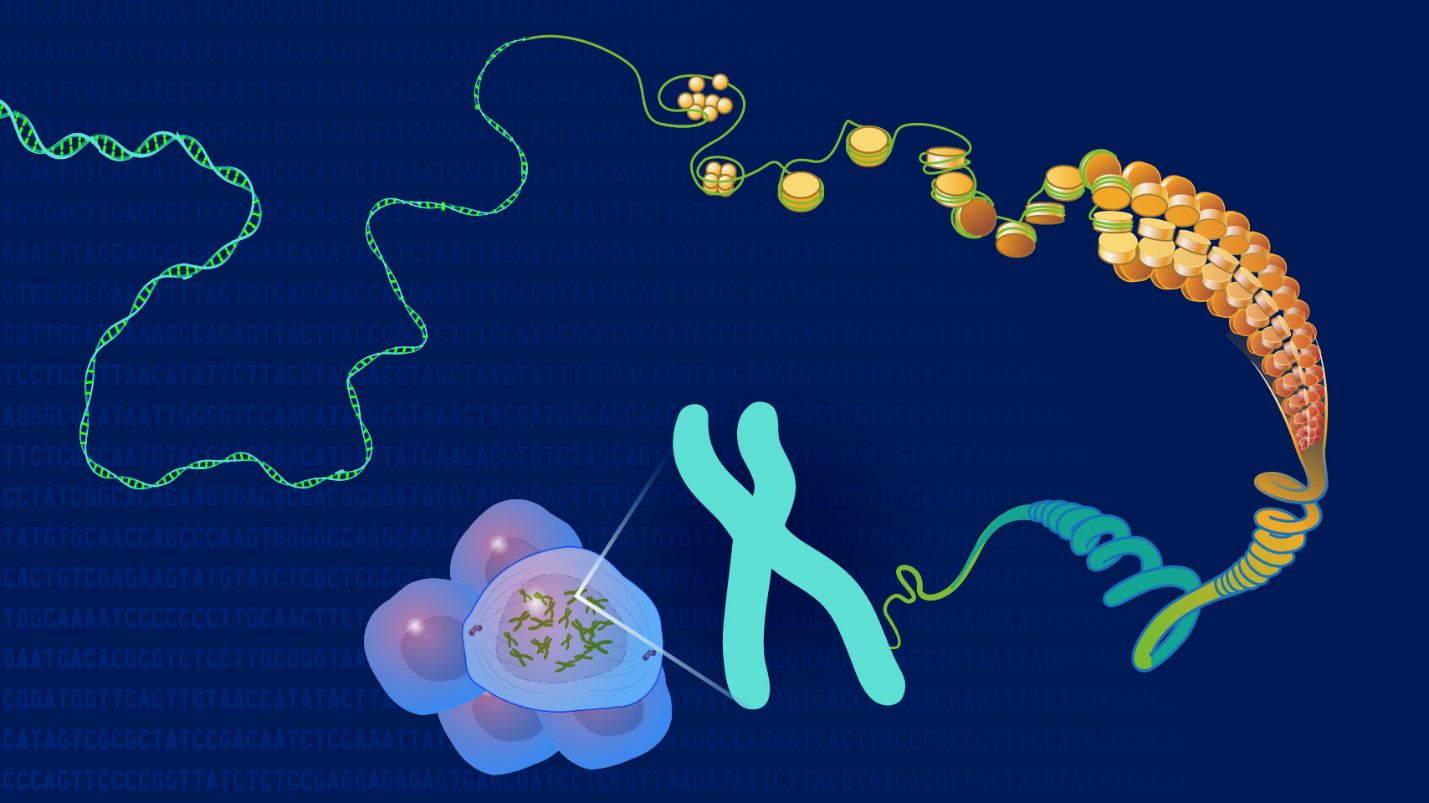
One of the cornerstones of personalized cancer treatment is genomics. By understanding the genetic mutations that drive cancer in individual patients, oncologists can tailor treatments to target those specific alterations. The Human Genome Project, completed in 2003, laid the foundation for this approach by mapping the entire human genome. Since then, technological advancements have made genomic sequencing faster and more affordable, enabling its integration into routine clinical practice.
Targeted Therapies
Targeted therapies are designed to interfere with specific molecules involved in cancer growth and progression. For example, drugs like imatinib (Gleevec) target the BCR-ABL fusion protein in chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), leading to remarkable remission rates. Similarly, trastuzumab (Herceptin) targets the HER2 protein in certain breast cancers, significantly improving outcomes. These therapies exemplify how understanding the genetic underpinnings of cancer can lead to more effective treatments.
Liquid Biopsies
Another promising development is the use of liquid biopsies, which analyze cancer-related genetic material in a patient’s blood. This non-invasive method allows for real-time monitoring of tumor evolution and treatment response. Liquid biopsies can detect minimal residual disease and emerging resistance mutations, enabling timely adjustments to therapy. As this technology matures, it is expected to become a standard tool in personalized cancer care.
The Rise of Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy harnesses the body’s immune system to fight cancer. Unlike traditional treatments, which directly target cancer cells, immunotherapy aims to enhance the immune system’s ability to recognize and destroy malignant cells. This approach has shown remarkable success in various cancers, including melanoma, lung cancer, and lymphoma.
Checkpoint Inhibitors
Checkpoint inhibitors are a class of immunotherapy drugs that block proteins used by cancer cells to evade the immune system. Drugs like pembrolizumab (Keytruda) and nivolumab (Opdivo) target the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway, unleashing the immune system to attack cancer cells. These treatments have led to durable responses and long-term remissions in some patients, even those with advanced disease.
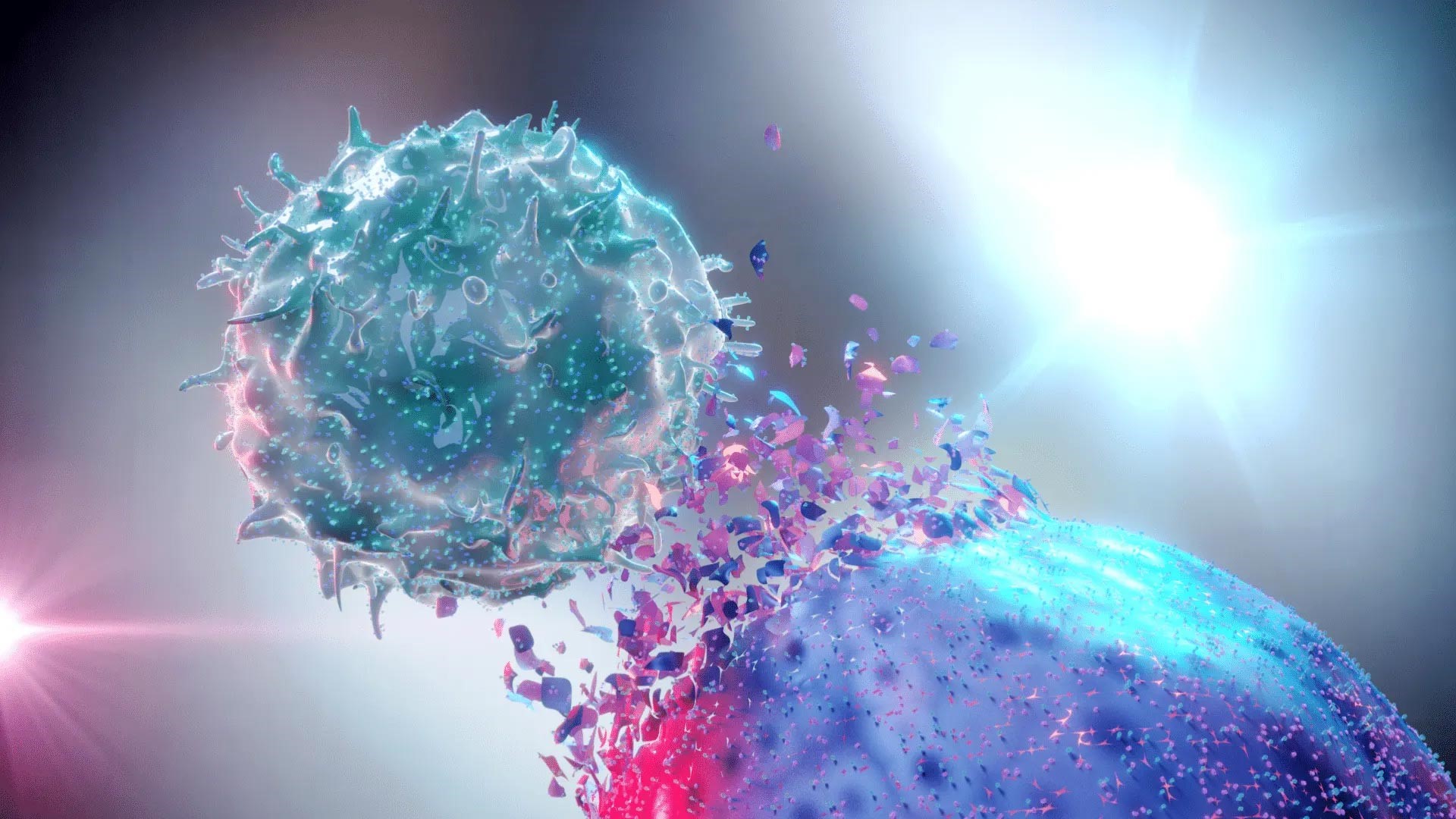
CAR-T Cell Therapy
Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-cell (CAR-T) therapy is another groundbreaking immunotherapy. This approach involves modifying a patient’s T-cells to express a receptor specific to cancer cells, then re-infusing these engineered cells back into the patient. CAR-T therapy has shown unprecedented success in treating certain blood cancers, such as acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL). Ongoing research aims to extend this success to solid tumors, which present a more complex challenge.
Artificial Intelligence and Big Data
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Big Data are poised to play transformative roles in personalized cancer treatments. AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of clinical and genomic data to identify patterns and predict treatment responses. This capability enables more accurate diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment planning.
Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics uses machine learning models to forecast how patients will respond to various treatments based on their unique genetic and clinical profiles. These models can help oncologists choose the most effective therapy with the least side effects, improving patient outcomes and quality of life.

Drug Discovery
AI is also accelerating drug discovery by identifying potential therapeutic targets and optimizing drug design. Machine learning algorithms can analyze complex biological data to uncover novel drug candidates and predict their efficacy and safety. This approach has the potential to significantly reduce the time and cost associated with bringing new cancer treatments to market.
Challenges and Future Directions
While the future of personalized cancer treatments is promising, several challenges remain. One significant hurdle is the heterogeneity of cancer. Tumors can vary widely between patients and even within the same patient over time. This complexity makes it difficult to develop universally effective treatments.
Access and Equity
Another challenge is ensuring equitable access to personalized treatments. Genomic sequencing, advanced immunotherapies, and AI-driven tools can be expensive and may not be readily available in all healthcare settings. Efforts must be made to democratize access to these cutting-edge therapies, ensuring that all patients benefit from advancements in cancer care.
Regulatory and Ethical Considerations
The integration of AI and genomics into clinical practice also raises regulatory and ethical questions. Ensuring the accuracy and reliability of AI algorithms is crucial, as is protecting patient privacy and data security. Regulatory frameworks must evolve to address these issues, fostering innovation while safeguarding patient interests.
Conclusion
The future of personalized cancer treatments is bright, driven by advancements in genomics, immunotherapy, and artificial intelligence. These innovations promise to transform cancer care, offering more effective and less toxic treatments tailored to individual patients. However, realizing this potential requires overcoming significant challenges, including cancer heterogeneity, access disparities, and regulatory hurdles. By addressing these issues, the medical community can ensure that the benefits of personalized cancer treatments reach all patients, ushering in a new era of oncology.