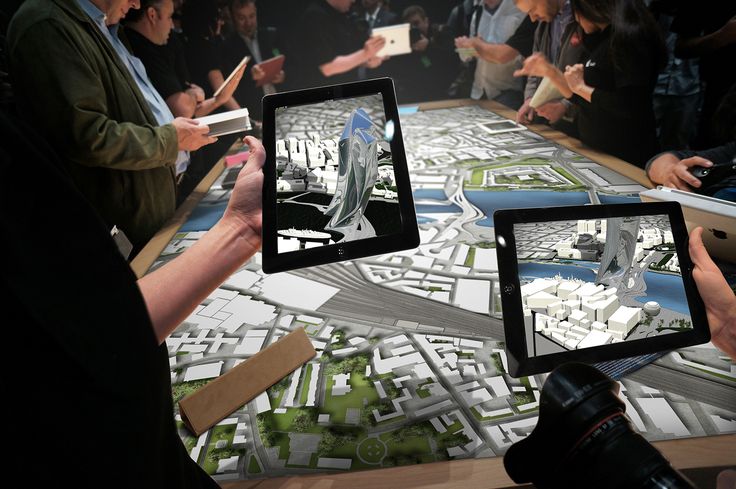
The Evolution of Augmented Reality
Augmented Reality (AR) has rapidly evolved into a technology that has transformed how we interact with the world around us. From its early beginnings in the 1960s to the immersive experiences of today, AR has reshaped industries and how we engage with digital content. This article will explore the history, development, and future potential of augmented reality, illustrating how it has become an essential part of modern technology.
1. The Birth of Augmented Reality

Augmented reality was first conceptualized by computer scientist Ivan Sutherland in the 1960s. He developed a system called the “Sketchpad,” which allowed users to interact with computer-generated images in real time. This early form of augmented reality was rudimentary but laid the foundation for future developments in AR technology. By the 1990s, the term “augmented reality” was coined by Tom Caudell, a researcher at Boeing, to describe a system used to assist workers in the assembly of aircraft by superimposing digital information onto physical objects.
2. The Rise of AR Technology in the 2000s
The 2000s saw a significant increase in the development of AR technology, driven by advances in computing power, mobile devices, and software. During this period, augmented reality was primarily used in specialized fields like healthcare, gaming, and military applications. For example, AR was utilized to help surgeons perform complex procedures by overlaying critical patient data onto their field of view. Similarly, the military used AR systems for training purposes, allowing soldiers to simulate combat scenarios in a controlled environment.
The launch of smartphones with built-in cameras and sensors marked a turning point for AR. This provided the perfect platform for AR applications to reach a wider audience. With the ability to interact with real-world environments, smartphones became the primary device for AR experiences.
3. The Introduction of AR in Gaming
Gaming has played a major role in the widespread adoption of augmented reality. One of the most significant milestones in AR gaming was the release of the game “Pokémon GO” in 2016. The mobile game blended the real world with virtual creatures, encouraging players to explore their surroundings in search of hidden Pokémon. The game’s success brought augmented reality into the mainstream, introducing millions of people to the potential of AR technology.
Pokémon GO demonstrated the immersive capabilities of AR, allowing users to interact with their environment in a way that was previously unimaginable. The game’s success has led to the development of other AR-based games, further establishing the technology’s place in the entertainment industry.
4. The Impact of Augmented Reality on Retail
Retail has also been transformed by augmented reality. Many brands now use AR to enhance the shopping experience, allowing customers to visualize products in their own space before making a purchase. For example, furniture stores like IKEA offer AR apps that allow users to see how a piece of furniture will look in their home environment by simply pointing their phone at the desired area.
Additionally, beauty brands have adopted AR technology to allow customers to “try on” makeup virtually. By using their phone’s camera, customers can see how different products will look on their skin without the need for physical application. This shift toward virtual try-ons has made shopping more convenient, personalized, and interactive.
5. Augmented Reality in Healthcare
Augmented reality has also found its place in healthcare, where it has proven to be a valuable tool in both medical education and patient treatment. Surgeons can use AR glasses to overlay essential data, such as CT scans or patient vitals, directly onto their view during procedures, improving accuracy and reducing the risk of errors. In medical training, AR is used to simulate real-life surgeries, allowing students to practice and develop their skills in a safe, controlled environment.
Beyond surgery, AR is being used to assist in physical rehabilitation. Patients recovering from injuries can engage in AR-based exercises that provide real-time feedback on their movements, helping them improve their range of motion and strength. This application of AR has revolutionized rehabilitation by making it more engaging and efficient.
6. The Role of AR in Education
The education sector has also benefited from the integration of augmented reality. AR can enhance the learning experience by creating interactive, immersive environments that bring abstract concepts to life. For example, students studying biology can use AR to visualize the human body in 3D, allowing them to explore its various systems and organs from different angles.
AR has also been used in classrooms to create interactive lessons and activities. For example, historical events can be brought to life through AR apps, allowing students to witness key moments in history as if they were present. This type of immersive learning can increase student engagement and retention by making education more dynamic and engaging.
7. The Future of Augmented Reality: AR Glasses
While smartphones and tablets have been the primary platforms for augmented reality, the future of AR is moving toward more wearable devices, such as AR glasses. Companies like Microsoft, Google, and Apple have been developing AR glasses that could one day replace the need for smartphones altogether. These glasses would display AR content directly in the user’s field of vision, creating a seamless and hands-free experience.
These AR glasses have the potential to revolutionize how we interact with digital content. For example, users could receive real-time information about their surroundings, such as navigation directions or information about nearby landmarks. Additionally, AR glasses could be used to enhance social interactions, allowing users to see real-time translations of foreign languages or provide contextual information about the people they are interacting with.
8. Challenges in AR Development
Despite the rapid growth and potential of augmented reality, there are still several challenges that need to be addressed. One of the biggest obstacles is the development of AR hardware that is both functional and comfortable. Current AR headsets and glasses tend to be bulky, limiting their adoption for everyday use. For AR to truly become mainstream, developers will need to create lightweight, stylish, and affordable devices that are comfortable to wear for extended periods.
Another challenge is the integration of AR with real-world environments. While AR has made significant progress, there are still issues with accurately mapping the physical world and ensuring that virtual objects interact realistically with their surroundings. Developers are working on improving AR tracking and mapping systems to overcome these issues, but it will take time to create fully immersive experiences that feel natural and intuitive.
9. Augmented Reality in Everyday Life

As AR technology continues to improve, it is becoming increasingly integrated into our daily lives. From virtual home tours to navigation systems that overlay directions onto the real world, AR is making it easier for people to access information and interact with their environment. For example, AR-powered navigation apps can guide drivers by overlaying directions on the windshield of a car, allowing them to keep their eyes on the road while receiving directions.
Furthermore, AR is being used in everyday activities such as fitness and cooking. AR fitness apps can guide users through exercises by superimposing instructional overlays onto their environment, while AR cooking apps can provide step-by-step instructions, visualizing the process and helping users prepare meals more efficiently.
10. The Future Potential of Augmented Reality
Looking ahead, augmented reality holds immense potential. As technology continues to advance, we can expect AR to become even more integrated into our lives, offering new ways to work, play, and interact with the world. One exciting possibility is the use of AR in smart cities, where digital information can be overlayed onto physical environments to help people navigate urban spaces more efficiently.
AR may also play a significant role in the development of the metaverse, a virtual world where users can interact with one another and digital environments in real time. In this new era of digital interaction, augmented reality will be a key component, enabling users to seamlessly switch between the physical and digital worlds.
Conclusion
The evolution of augmented reality has been nothing short of remarkable. From its humble beginnings in the 1960s to its widespread use today, AR has transformed how we interact with technology and the world around us. As AR continues to evolve, its potential to enhance industries like gaming, retail, healthcare, education, and more will only continue to grow. With ongoing advancements in hardware and software, the future of augmented reality promises to be even more immersive and life-changing.




