Introduction
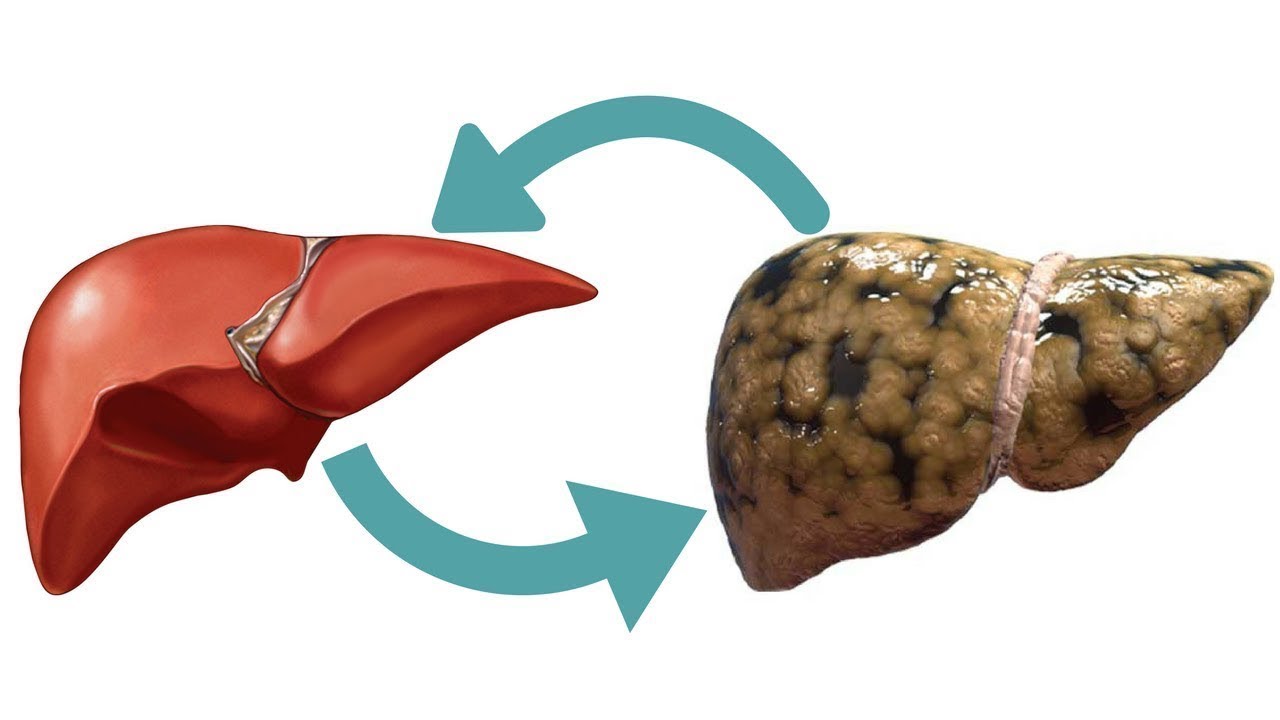
The liver, a vital organ in the human body, plays a crucial role in metabolism, digestion, and detoxification. However, in recent years, the prevalence of fatty liver disease has been on the rise, posing significant health risks to individuals worldwide. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and prevention methods of liver disease is essential for maintaining optimal liver health and overall well-being.
What is Fatty Liver Disease?
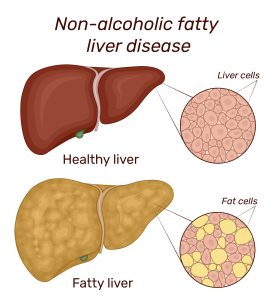
Fatty liver disease, also known as hepatic steatosis, is a condition characterized by the accumulation of fat in the liver cells. This excess fat can lead to inflammation and damage to the liver tissue, impairing its ability to function properly. There are two main types of fatty liver disease:
Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
NAFLD is the most common form of fatty liver disease and is not related to excessive alcohol consumption. It typically develops in individuals who are overweight or obese, have insulin resistance, or have high levels of fat in the blood. NAFLD can progress to more severe liver conditions, such as non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), cirrhosis, and liver cancer.
Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (AFLD)
AFLD is caused by excessive alcohol consumption and is often seen in individuals who engage in heavy drinking over an extended period. Alcohol is metabolized in the liver, and chronic alcohol abuse can lead to the accumulation of fat, inflammation, and liver damage.
Understanding the Risk Factors
Several factors contribute to the development of fatty liver disease, including:
- Obesity: Excess body weight, especially abdominal fat, increases the risk of NAFLD.
- Insulin Resistance: Insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes are closely linked to fatty liver disease.
- High Cholesterol: Elevated levels of cholesterol and triglycerides in the blood can contribute to liver fat accumulation.
- Poor Diet: Diets high in sugar, refined carbohydrates, and unhealthy fats can promote liver fat deposition.
- Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of physical activity is associated with an increased risk of NAFLD.
- Genetics: Some genetic factors may predispose individuals to fatty liver disease.
- Alcohol Consumption: Excessive alcohol intake is a major risk factor for AFLD.
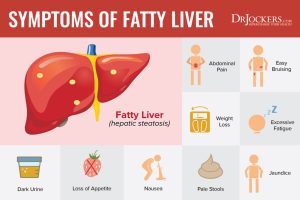
Recognizing the Symptoms
Fatty liver disease is often asymptomatic in its early stages, but as the condition progresses, individuals may experience symptoms such as:
- Fatigue
- Weakness
- Abdominal pain or discomfort
- Elevated liver enzymes
- Enlarged liver
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
It is important to note that not everyone with fatty liver disease will experience symptoms, and the condition may only be detected through routine medical tests.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options
Diagnosing fatty liver disease typically involves a combination of medical history review, physical examination, and diagnostic tests, including blood tests, imaging studies (such as ultrasound or MRI), and sometimes liver biopsy. Treatment strategies for fatty liver disease aim to:
- Manage underlying conditions: Controlling conditions such as obesity, diabetes, and high cholesterol can help prevent further liver damage.
- Lifestyle modifications: Adopting a healthy diet, increasing physical activity, and avoiding alcohol can improve liver health and reduce fat accumulation.
- Medications: In some cases, medications may be prescribed to help control symptoms or manage underlying conditions associated with fatty liver disease.
- Monitoring and follow-up: Regular monitoring and follow-up with a healthcare provider are essential to track the progression of the disease and make necessary adjustments to treatment plans. Explore More About ( Link Between Diabetes or Fast Walking)
Prevention is Key
Preventing fatty liver disease involves making lifestyle changes that promote liver health and overall well-being. Here are some tips to help reduce the risk of developing fatty liver disease:
Maintain a Healthy Weight
- Aim for a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Limit intake of sugary beverages, processed foods, and foods high in saturated and trans fats.
- Engage in regular physical activity, such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming, for at least 30 minutes a day.
Monitor Alcohol Intake
- Limit alcohol consumption to moderate levels: up to one drink per day for women and up to two drinks per day for men.
- Avoid binge drinking or excessive alcohol consumption, especially on a regular basis.
Manage Medical Conditions
- Keep diabetes, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol under control through medication, diet, and lifestyle modifications.
- Follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations for regular check-ups and screenings.
Seek Support and Guidance
- If you’re struggling to make lifestyle changes on your own, consider seeking support from a healthcare provider, nutritionist, or counselor.
- Joining support groups or online communities can also provide encouragement and motivation on your journey to better health.
NAFLD vs. AFLD
| Aspect | NAFLD | AFLD |
|---|---|---|
| Cause | Obesity, insulin resistance, high blood fat levels | Excessive alcohol consumption |
| Relationship with alcohol | Not related | Directly caused by alcohol intake |
| Risk factors | Obesity, insulin resistance, high blood fat levels, sedentary lifestyle | Excessive alcohol consumption |
| Progression | Can progress to NASH, cirrhosis, liver cancer | Can lead to alcoholic hepatitis, cirrhosis, liver failure |
| Treatment | Lifestyle modifications, medication | Abstinence from alcohol, supportive care |
Conclusion
Fatty liver disease is a common yet preventable condition that can have serious consequences if left untreated. By understanding the risk factors, recognizing the symptoms, and taking proactive steps to maintain liver health, individuals can reduce their risk of developing fatty liver disease and improve their overall quality of life. Remember, a healthy liver is essential for optimal health and well-being, so prioritize your liver health today for a healthier tomorrow.