In the world of milk choices, cow’s milk, almond milk, and soy milk are some of the most popular options. Each type of milk offers distinct nutritional benefits, making the decision of which to include in your diet a matter of personal preferences and dietary needs. In this comparison, we will explore the nutritional benefits of cow’s milk, almond milk, and soy milk to help you determine which might be the healthiest choice for you.
Cow’s Milk: The Classic Option
Nutritional Highlights:
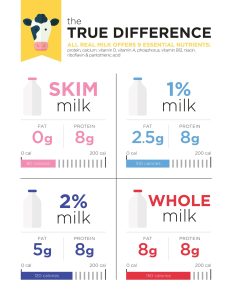
- Protein: Cow’s milk is an excellent source of complete protein, providing all the essential amino acids required by the body. A single 8-ounce cup of cow’s milk contains about 8 grams of protein.
- Calcium: Cow’s milk is rich in calcium, promoting bone health. An 8-ounce serving typically provides around 300 mg of calcium.
- Vitamins and Minerals: Cow’s milk is a good source of vitamins and minerals, including vitamin D, vitamin B12, and riboflavin.
- Fats: Depending on the type (whole, 2%, 1%, or skim), cow’s milk can be higher in saturated fats (whole milk) or lower in fats (skim milk).
https://cdn1.gonnaneedmilk.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/03/07055854/0001_0-scaled.jpg
Almond Milk: A Dairy-Free Alternative
Nutritional Highlights:
- Low in Calories: Unsweetened almond milk is low in calories, making it an ideal choice for those seeking to manage their calorie intake.
- Low in Saturated Fat: Almond milk is naturally low in saturated fat, making it heart-healthy.
- Nutrients: Many commercial brands fortify almond milk with calcium, vitamin D, and vitamin E. However, the nutrient content may vary between brands.
- Lactose-Free: Almond milk is naturally lactose-free, making it suitable for those with lactose intolerance.
Soy Milk: A Plant-Based Powerhouse
Nutritional Highlights:
- Protein: Soy milk is one of the plant-based milk options that comes closest to cow’s milk in terms of protein content. It provides all essential amino acids.
- Calcium: Many brands fortify soy milk with calcium, offering a calcium content similar to cow’s milk.
- Vitamins and Minerals: Soy milk can be fortified with vitamins like vitamin D and vitamin B12, making it a well-rounded option.
- Soy Isoflavones: Soy milk contains compounds called isoflavones, which have been associated with various health benefits, including heart health.
- Lactose-Free: Like almond milk, soy milk is naturally lactose-free.
How to Choose the Healthiest Option
The healthiest milk option for you depends on your dietary needs, preferences, and health goals:
- Cow’s Milk: Choose cow’s milk if you are looking for a complete protein source and you are not lactose intolerant. Opt for lower-fat versions if you want to reduce saturated fat intake.
- Almond Milk: Select almond milk if you are vegan, lactose intolerant, or seeking a low-calorie milk option. Be sure to choose unsweetened varieties to avoid added sugars.
- Soy Milk: Opt for soy milk if you prefer a plant-based option with protein content similar to cow’s milk. It is suitable for vegans and those with lactose intolerance.
https://www.organicfacts.net/wp-content/uploads/typesofmilk.jpg
Conclusion
The choice between cow’s milk, almond milk, and soy milk ultimately depends on your dietary preferences and nutritional needs. Each type of milk has its own set of advantages, whether you prioritize complete protein, low calories, or plant-based options. To make the healthiest choice, assess your dietary goals and consider factors such as lactose intolerance, calorie intake, and taste preferences. Whichever milk you choose, be mindful of the added ingredients, such as sugars or artificial additives, in commercial varieties. Consulting with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian can provide personalized guidance in selecting the milk that best aligns with your individual dietary requirements and health objectives.