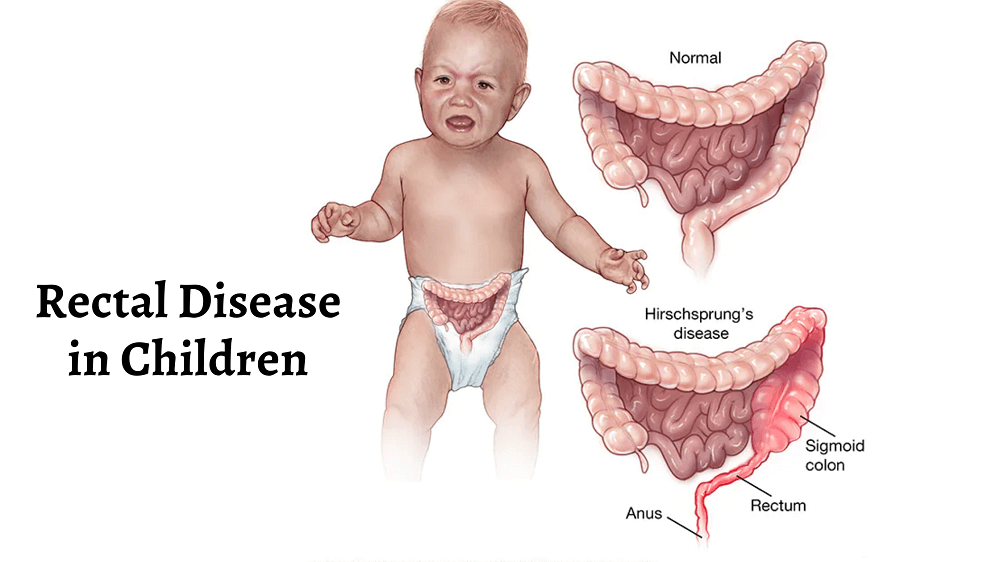
Introduction:
Navigating the intricacies of rectal bleeding in children requires a comprehensive understanding of the various factors at play. This article aims to provide a thorough exploration of the common causes, symptoms, diagnostic approaches, and treatment considerations associated with rectal bleeding in the pediatric population.
The Occurrence of Rectal Bleeding in Children:
Understanding the Prevalence:
Rectal bleeding in children, though relatively infrequent, prompts heightened concern among parents. Unlike in adults, the exact prevalence remains elusive, underscoring the need for nuanced examination when symptoms arise.
Recognizing the Importance of Timely Intervention:
When to Worry About Rectal Bleeding:
While rectal bleeding in children often stems from benign causes, the paramount importance of seeking professional medical advice cannot be overstated. Timely consultation with a healthcare professional is vital to rule out serious conditions, allowing for precise diagnosis and appropriate intervention.
A Spectrum of Causes in Pediatric Rectal Bleeding:
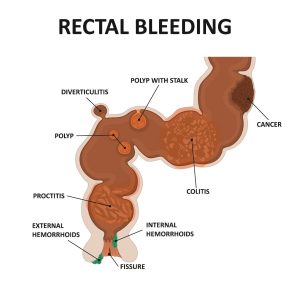
Common Causes:
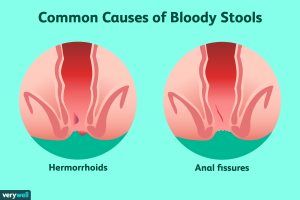
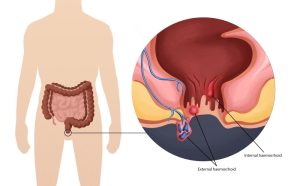
- Anal Fissure:
- Frequently observed in babies and children, often triggered by the passage of large or hard stools.
- Manifests as bright red blood in stools, accompanied by pain.
- Generally resolves with conservative measures, such as stool softening.
- Twisting of the Gut (Volvulus):
- Involves a loop of bowel twisting around itself, potentially compromising blood supply.
- Symptoms may include rectal bleeding, vomiting, and abdominal swelling.
- Intussusception:
- More prevalent in infants aged 5-7 months.
- Presents with recurrent episodes of abdominal pain, vomiting, and abdominal swelling.
- Bowel Polyps:
- Characterized by painless, recurrent bleeding; typically benign.
- Meckel’s Diverticulitis:
- Congenital bulge in the gut wall.
- Inflammation may lead to rectal bleeding, with higher incidence in boys aged under 2.
Serious Conditions:
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD):
- Encompasses chronic inflammation of the digestive tract, including Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis.
- Gastroenteritis:
- Infectious origin resulting in symptoms like diarrhea, vomiting, and potential rectal bleeding.
Rarer Causes:
- Necrotising Enterocolitis:
- A grave condition involving inflammation and tissue necrosis in the gut; rare in newborns.
- Sexual Abuse:
- May manifest with rectal bleeding, necessitating careful consideration in certain cases.
- Hirschsprung’s Enterocolitis:
- Arises from nerve cell dysfunction, causing gut blockage; associated with severe complications.
- Vascular Abnormalities:
- Encompass various lesions like haemangiomas, arteriovenous malformations, and angiodysplasias, posing diagnostic challenges.
- Henoch-Schönlein Purpura:
- Provokes inflammation and bleeding in small blood vessels.
- Haemolytic Uraemic Syndrome (HUS):
- Originating from abnormal red blood cell breakdown, HUS poses a serious threat, manifesting as abnormal bleeding, including rectal bleeding.
- Low Blood Platelets (Thrombocytopenia):
- A condition marked by a decreased platelet count, potentially leading to abnormal bleeding, including rectal bleeding.
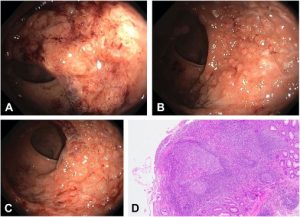
Unraveling the Symptomatic Tapestry:
Variability in Symptoms:
- Blood Appearance:
- Bright red blood suggests lower gut bleeding.
- Dark red or black stools indicate upper gut bleeding (melaena).
- Stomach bleeding may lead to vomiting of blood (haematemesis).
- Consistency of Symptoms:
- Rectal bleeding may manifest with variable severity, presenting intermittently or persistently.
- Regardless of the volume or frequency of bleeding, seeking professional evaluation remains imperative.
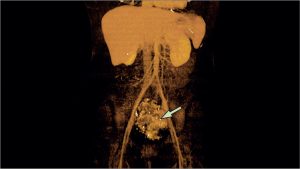
Navigating the Diagnostic Landscape:
Comprehensive Testing:
- Initial Tests:
- Blood tests and stool examination serve as preliminary diagnostic measures.
- Advanced Investigations:
- Further assessments may include X-rays, ultrasound, CT, or MRI scans.
- In certain cases, a colonoscopy under general anesthesia might be warranted.
Tailoring Treatment to the Underlying Cause:
Individualized Approaches:
- Treatment Paradigm:
- The course of treatment hinges on the underlying cause and the severity of bleeding.
- Minor cases may self-resolve without intervention.
- Ambiguous or severe cases necessitate referral to specialists for in-depth evaluation and management.
Understanding Prognosis:
A Glimpse into the Future:
- Prognostic Considerations:
- The outlook depends on the underlying cause of rectal bleeding.
- Most instances in children lean towards a favorable prognosis, often resolving without specific interventions.
Conclusion
The journey through the intricate landscape of rectal bleeding in children unveils a spectrum of causes, symptoms, and considerations that underscore the need for vigilant parental attention and timely medical intervention. While rectal bleeding in the pediatric population is relatively uncommon, its potential to evoke anxiety in parents necessitates a thorough understanding of the nuanced factors at play.
The varied causes, ranging from benign conditions like anal fissures to more serious underlying issues such as inflammatory bowel disease or vascular abnormalities, emphasize the importance of seeking professional medical advice. The pivotal question of “when to worry” underscores the need for a healthcare professional’s insight, allowing for precise diagnosis and tailored intervention strategies.
Understanding the symptomatic tapestry, diagnostic landscape, and individualized treatment approaches is crucial in navigating the complexities associated with rectal bleeding in children. Bright red blood or dark stools may hold clues to the origin of bleeding, and the variability in symptom presentation necessitates a comprehensive evaluation, including blood tests, stool examinations, and advanced imaging studies.