Introduction to Ringworm
What is Ringworm?
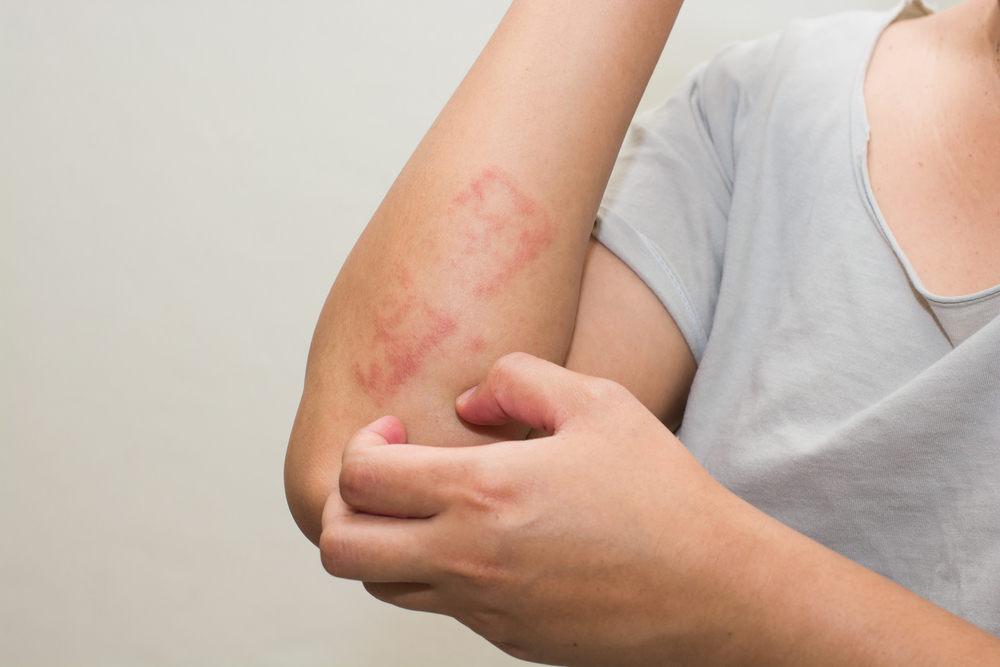
Ringworm Unmasked, also known as dermatophytosis, is a contagious fungal infection that can affect the skin, scalp, and nails. It is characterized by red, itchy patches that may resemble a ring, hence the name “ringworm.”
Why is it called “Ringworm”?
Despite its name, nothing to do with worms. The term “ringworm” originated from the appearance of the infection on the skin, which often forms a circular or ring-like pattern.

Types of Ringworm Infections
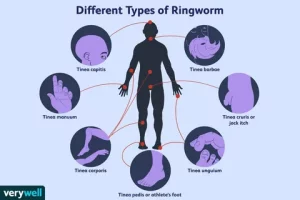
Ringworm can manifest in various forms, each affecting different parts of the body. Some common types of ringworm infections include:
Dermatophyte Infections
Dermatophytes are a group of fungi that cause infections. They thrive in warm, moist environments and can infect the skin, scalp, and nails.
Scalp Ringworm (Tinea Capitis)
Scalp ringworm, also known as tinea capitis, is a fungal infection that affects the scalp and hair follicles. It is most common in children and can lead to hair loss and scalp inflammation.
Body Ringworm (Tinea Corporis)
Body, or tinea corporis, is a fungal infection that affects the skin on the body. It typically appears as red, circular patches that may be itchy or scaly.
Jock Itch (Tinea Cruris)
Jock itch, or tinea cruris, is a fungal infection that affects the groin and inner thighs. It is common in athletes and individuals who sweat heavily in the groin area.
Athlete’s Foot (Tinea Pedis)
Athlete’s foot, or tinea pedis, is a fungal infection that affects the feet. It can cause itching, burning, and peeling of the skin, particularly between the toes.
Causes and Transmission
caused by fungi known as dermatophytes, which thrive in warm, moist environments. These fungi can be transmitted through various means, including:
Fungal Sources
Ringworm fungi can be found in soil, on infected humans or animals, and on contaminated surfaces such as towels, clothing, and sports equipment.
Human-to-Human Transmission
Direct skin-to-skin contact with an infected individual can transmit from one person to another.
Animal-to-Human Transmission
Pets, particularly cats and dogs, can carry fungi on their fur and skin, leading to transmission to humans.
Symptoms
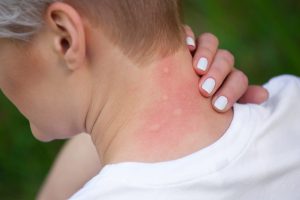
infections can present a variety of symptoms, depending on the type and location of the infection. Common symptoms include:
- Itchy Red Patches
- Circular Rash
- Peeling, Cracking, or Scaling Skin
- Hair Loss (in Scalp Ringworm)
Prevention Tips
While ringworm is highly contagious, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk of infection:
- Maintain Good Hygiene Practices
- Avoid Sharing Personal Items
- Keep Skin Clean and Dry
- Wear Protective Clothing in Public Areas Explore More About Health
Treatment Options
Treatment for typically involves antifungal medications to eliminate the fungi causing the infection. Depending on the severity and location of the infection, treatment options may include:
- Over-the-Counter Antifungal Medications
- Prescription Medications
- Topical Creams and Ointments
- Home Remedies and Natural Treatments
Complications of Untreated
Without proper treatment, infections can lead to various complications, including:
- Spread to Other Body Parts
- Secondary Bacterial Infections
- Permanent Hair Loss
Specific Populations
Certain populations may be more susceptible to infections, including:
- Children
- Athletes
- Pet Owners
When to See a Doctor
While most cases can be treated at home, you should consult a doctor if:
- Persistent Symptoms
- Complications
- Treatment Not Working

Conclusion
common fungal infection that can affect anyone, regardless of age or gender. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for, you can take proactive steps to prevent infection and promote healing if you or a loved one are affected.