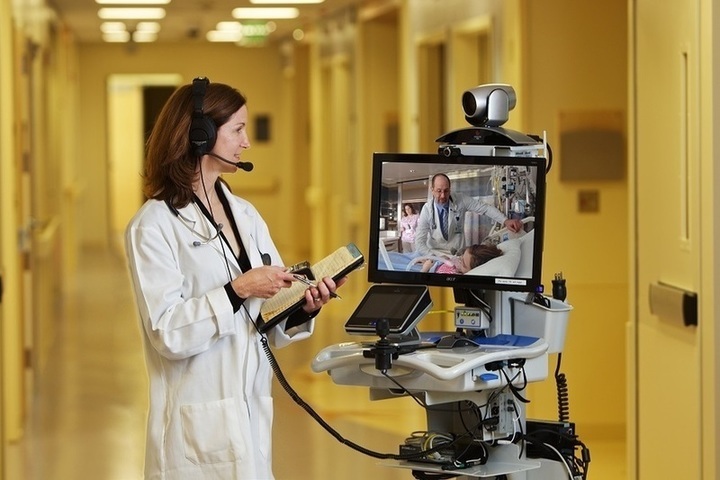
In recent years, telemedicine has transformed the healthcare landscape, creating a paradigm shift in how healthcare services are delivered. The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated its adoption, but its continued growth in 2024 is driven by advancements in digital health solutions, Artificial Intelligence (AI), and increased demand for accessible and convenient healthcare. This article provides an in-depth analysis of telemedicine’s evolution, benefits, challenges, and future directions, with real-world examples and case studies that highlight its transformative impact.
1. What is Telemedicine?

Telemedicine refers to the remote delivery of healthcare services via technology, allowing patients and providers to connect virtually for consultations, diagnosis, and treatment. It encompasses various digital platforms and technologies, including video consultations, mobile health applications, remote patient monitoring (RPM), and wearable devices that track health metrics. Telemedicine aims to make healthcare more accessible and efficient, particularly for individuals in remote or underserved areas.
2. Benefits of Telemedicine Growth
A. Enhanced Access to Healthcare
One of the most significant advantages of telemedicine is the expanded access to healthcare services. Patients in rural or remote areas, where healthcare facilities are limited, can now access specialists and primary care providers without needing to travel. According to the American Hospital Association, over 60% of hospitals in the U.S. offer some form of telemedicine, helping bridge the gap for rural patients.
Example:
Consider a patient living in a rural town who requires a dermatology consultation. Without telemedicine, they might need to travel several hours to the nearest city. With telemedicine, the patient can receive a consultation via video, allowing for quicker diagnosis and treatment.
B. Improved Patient Outcomes through Real-Time Monitoring
Wearables and IoT-enabled devices have revolutionized telemedicine by enabling continuous monitoring of patient health metrics. Real-time health data, such as heart rate, blood pressure, and blood glucose levels, can be transmitted to healthcare providers, who can respond quickly to any abnormalities. This continuous monitoring has proven particularly beneficial for managing chronic conditions such as diabetes and hypertension.
Case Study: Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM)
A study conducted by Kaiser Permanente found that telemedicine-based RPM reduced hospital admissions for patients with heart disease by 40%. By providing proactive care based on real-time data, patients can avoid complications that may require hospitalization.
C. Cost Savings for Patients and Providers

Telemedicine can reduce healthcare costs by decreasing the need for in-person visits, reducing travel expenses for patients, and allowing healthcare providers to manage their time more efficiently. Additionally, many telehealth platforms offer cost-effective consultations, making healthcare more affordable for uninsured or underinsured patients.
Example: Cost Comparison
For example, a virtual consultation costs about $50 on average, while an in-person visit can cost upwards of $150. These savings can significantly benefit individuals requiring frequent check-ups or those without comprehensive health insurance.
D. Enhanced Patient Engagement and Convenience
Telemedicine provides a convenient alternative for patients, particularly those with busy schedules or mobility issues. The ease of accessing healthcare from home can improve patient engagement and adherence to treatment plans. Research by McKinsey found that 55% of patients preferred virtual visits due to convenience.
3. Challenges Facing Telemedicine Growth
Despite its benefits, telemedicine faces several challenges that could hinder its growth and adoption:
A. Regulatory and Privacy Concerns
Telemedicine operates within a complex regulatory landscape. Issues such as patient data privacy, HIPAA compliance, and licensing across state lines can create barriers. For instance, telemedicine providers must ensure secure communication channels to protect patient data. Failure to comply with data security laws can lead to legal issues and loss of patient trust.
B. Digital Divide and Accessibility
While telemedicine offers greater access to healthcare, it also exacerbates the “digital divide.” Patients who lack digital literacy or access to reliable internet connections may find it challenging to use telemedicine services. A study by Pew Research found that 38% of rural Americans do not have reliable internet, which limits their access to telemedicine.
C. Over-Reliance on Virtual Care
There are concerns that telemedicine could lead to an over-reliance on virtual care, potentially compromising the quality of diagnosis and treatment for conditions requiring physical examination. Many healthcare providers advocate a hybrid model, combining virtual consultations with in-person visits as needed.
4. Telemedicine Growth Trends in 2024
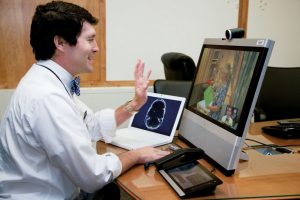
The growth of telemedicine in 2024 is largely driven by technological advancements. Key trends include:
A. AI and Machine Learning for Enhanced Diagnostics
AI-powered tools are being integrated into telemedicine platforms to improve diagnostics and personalize patient care. For example, AI algorithms can analyze radiology images or detect patterns in patient data, aiding providers in early diagnosis.
Example:
Teladoc Health, a leading telemedicine provider, has introduced AI-powered tools that assist in diagnosing skin conditions through image analysis. By using machine learning models, Teladoc can provide faster and more accurate diagnoses remotely.
B. Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) in Consultations
Virtual reality and augmented reality are being used to create immersive telemedicine experiences. VR can facilitate remote physical therapy sessions, while AR can assist surgeons during consultations by overlaying digital images onto a real-world view.
Case Study: VR in Physical Therapy
A pilot program at a rehabilitation center utilized VR headsets to guide patients through physical therapy exercises remotely. Patients reported higher engagement and adherence to their therapy routines, showcasing VR’s potential in telemedicine.
C. Wearable Devices and IoT Integration
Wearables, such as smartwatches and fitness trackers, allow for real-time health monitoring and seamless data integration with telemedicine platforms. This integration enables healthcare providers to monitor patients’ vital signs remotely, alerting them to potential health risks in real time.
5. Future Outlook for Telemedicine
As telemedicine continues to evolve, its growth trajectory is expected to remain strong. Key areas for future development include:
A. Expansion into New Specialties
Telemedicine is expanding into specialties such as dermatology, psychiatry, and chronic disease management. These fields benefit from remote consultations and real-time monitoring, providing more accessible care for patients.
B. Increased Focus on Hybrid Healthcare Models
Healthcare providers are likely to adopt hybrid models that blend virtual and in-person care. This model provides the flexibility of telemedicine while ensuring patients have access to hands-on examinations when necessary.
C. Advances in Data Security and Privacy
As telemedicine becomes more prevalent, advances in cybersecurity will be crucial to protect patient data. Emerging technologies, such as blockchain, may play a role in securing telehealth platforms and ensuring compliance with data privacy regulations.
Telemedicine Adoption in Rural Healthcare

A notable case study involves the adoption of telemedicine in a rural hospital network in Texas. This network faced a shortage of specialists, particularly for cardiology and psychiatry. By partnering with telemedicine providers, the hospital was able to offer virtual consultations with specialists, improving patient outcomes and reducing hospital transfers by 30%.
This case underscores the potential of telemedicine to bridge healthcare gaps in underserved communities. Patients benefited from timely access to specialists, while the hospital could expand its service offerings without needing to hire full-time specialists.
Conclusion
Telemedicine has revolutionized healthcare delivery, offering significant benefits in terms of access, cost savings, and patient engagement. However, its growth is accompanied by challenges, including regulatory complexities, digital divides, and the need for cybersecurity. As the telemedicine landscape continues to evolve in 2024, advancements in AI, VR, and IoT will further enhance its capabilities, making healthcare more accessible and efficient.
The future of telemedicine lies in hybrid models that combine the best of virtual and in-person care. By addressing current challenges and leveraging new technologies, telemedicine can continue its trajectory toward becoming a mainstream mode of healthcare delivery.




