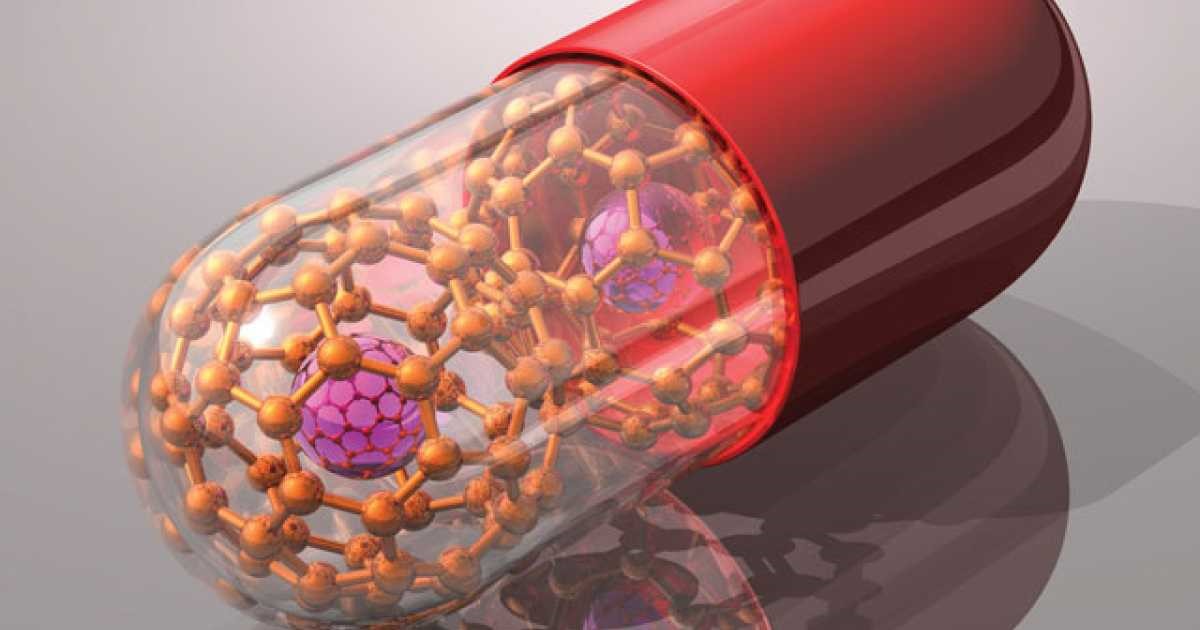
Nanotechnology has revolutionized drug delivery systems, offering precise targeting, enhanced efficacy, and reduced side effects. This article explores the transformative impact of nanoscience on drug delivery, highlighting key advancements, applications, and future prospects.
1. Understanding Nanotechnology in Drug Delivery
Nanoscience involves manipulating materials at the nanoscale (1-100 nanometers) to create structures with unique properties. In drug delivery, nanoparticles are designed to encapsulate drugs and deliver them to specific cells or tissues.
2. Enhancing Bioavailability and Targeting
Nanoparticles improve drug solubility and stability, enhancing bioavailability and enabling targeted delivery to diseased tissues or organs. Surface modifications allow nanoparticles to evade immune detection and selectively bind to target sites.
3. Overcoming Biological Barriers
Nanotechnology addresses biological barriers such as the blood-brain barrier, improving drug penetration into tissues that were previously inaccessible. This capability is crucial for treating neurological disorders and cancers.
4. Controlled Release Mechanisms
Nanoparticles enable controlled release of drugs over time, maintaining therapeutic levels in the body and reducing dosing frequency. This controlled delivery minimizes side effects and improves patient compliance.
5. Multifunctional Nanocarriers
Advancements in nanotechnology have led to the development of multifunctional nanocarriers. These carriers can combine therapeutic agents with diagnostic or imaging agents, facilitating theranostic applications in personalized medicine.
6. Targeted Cancer Therapy
Nanotechnology plays a pivotal role in targeted cancer therapy. Nanoparticles can selectively deliver chemotherapy drugs to tumors while sparing healthy tissues, minimizing systemic toxicity and enhancing treatment efficacy.
7. Challenges in Nanotechnology-Based Drug Delivery
Despite its promise, nanoscience faces challenges such as scalability, manufacturing complexity, and long-term safety concerns. Addressing these challenges is crucial for translating research into clinical applications.
8. Nanotechnology in Vaccines
Nanoparticles are being explored in vaccine delivery to enhance immune responses and vaccine stability. nanoscience -based vaccines have the potential to combat infectious diseases more effectively.
9. Regulatory Considerations and Safety
Regulatory agencies evaluate nanotechnology-based drug delivery systems for safety, efficacy, and manufacturing standards. Understanding regulatory requirements is essential for advancing nanomedicine from lab to market.
10. Future Directions and Innovations

The future of nanotechnology in drug delivery is promising. Emerging trends include nano-robotics for precise drug targeting, smart nanoparticles for responsive drug release, and personalized nanomedicine tailored to individual genetic profiles.
Conclusion
In conclusion, nanotechnology has transformed drug delivery systems, offering unprecedented capabilities in targeted therapy, controlled release, and enhanced treatment outcomes. Continued research and innovation are essential for overcoming challenges and realizing the full potential of nanoscience in improving global healthcare.