The MSConfig is an Microsoft System Configuration Utility
MSConfig is the system configuration utility made by Microsoft. Despite being widely unknown and very efficient. Users can change startup settings through this tool MSConfig is a terrific troubleshooting and repair tool since it lets you choose which programs and services should launch while Windows loads.
Implement Clean Boot With MSConfig
The System Configuration Utility is designed for performing a clean boot. A clean boot starts your device with just the essential Microsoft services, preventing any third-party services or applications from running. This facilitates locating and correcting conflicts between disparate applications To perform a clean boot, follow these steps:
Hit Windows key + R to trigger the Run dialog box
Hit Enter to open the MSConfig window after typing “msconfig”.
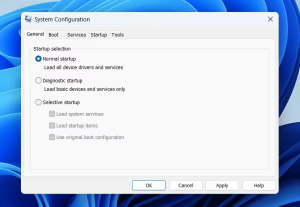
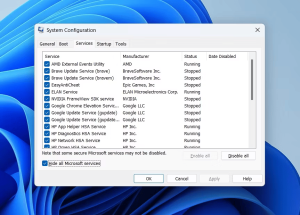
You must access the Services tab on the MSConfig window.
Unmark the check-box to conceal Microsoft’s fundamental offerings.
By selecting ‘Disable all’, you can shut down all non-Microsoft services.
Select the Startup tab prior to launching the task manager.
Do not enable unneeded programs that launch during start up
MSConfig window will ask you to close Task Manager before proceeding; follow it.
Start your computer anew and approve your modifications.
Choosing the Default Operating System
Using MSConfig, multiple Windows versions can be designated the preferred OS by a single user. Here’s how to do it:
Launch the MSConfig screen as described previously
Navigate to the “Boot” tab.
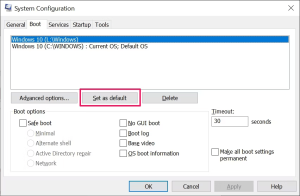
The desired operating system should be chosen here.
The button ‘Set as Default’ is your choice.

Enter the number of seconds (value) into the field to customize the Timeout for Windows to load the default OS.
“Apply” and “OK” are options for saving your changes.
Allocating Processor Cores with MSConfig
Users may allocate a particular number of processor cores with the System Configuration Utility. Follow these steps to allocate processor cores:
In MSConfig, navigate to its Boot tab.
Set the default operating system to display by choosing it, then clicking on “Advanced options.”,
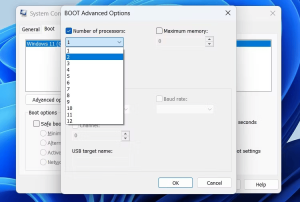
Go ahead and select the box adjacent to “Number of processors.”
You can choose the number of processors for allocation from the drop-down menu.
Applying edits requires three button-clicks.
Boosting to secure mode through MSConfig
Windows initiates in Safe Mode by providing merely crucial services and drivers, therefore making it convenient to resolve computer hardware and software issues. To boot into Safe Mode using MSConfig, follow these steps:
Choose Boot when you click MSConfig.
In the “Boot options” section, check “Safe boot.”
Options for starting Safe Mode include minimal, networking, or command prompt.
Select OK and restart afterwards.
MSConfig explores the other boot tab settings.
In addition to the aforementioned features, the Boot tab in MSConfig offers several other settings that can optimize system performance:
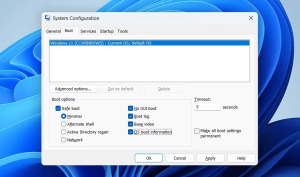
No GUI Boot: Prevents you from checking whether your system stalled during boot but still enables the fast boot.
Boot Log: It generates a text file containing the information about expected driver names that were not loaded during boot.
Base Video: Re-boots the machine with a video driver preinstalled.
OS Boot Information: shows active drivers during booting; used alongside ‘No GUI Boot’ for displaying driver information.
Using MSConfig to Operate Different Tools
Common Windows utilities can be accessed from the ‘Tools’ tab of System Configuration Utility. Here’s how to access them:
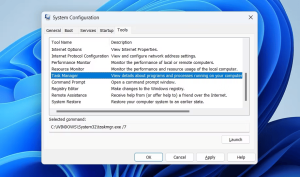
Access MSConfig using the Tools tab.
Pick a utility to begin, and select ‘Launch’.
Conclusion
You may customize your Windows OS with the MSConfig utility. With MSConfig you can configure boot options and resolve problems, or access diagnostic tools that help to optimize computer performance. At the next instance of a problem, examine MSConfig’s functions that help diagnose and remedy it.




