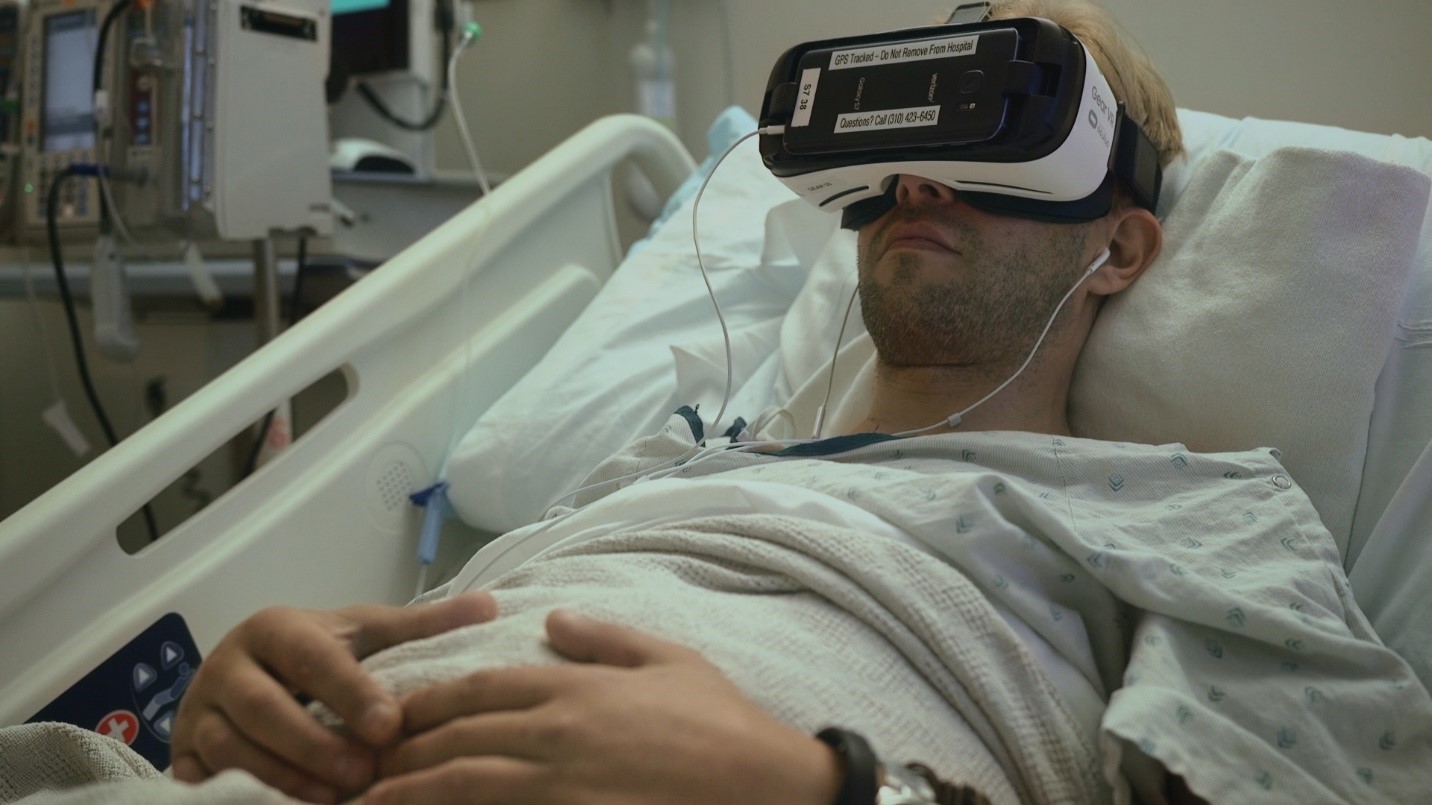
In recent years, the landscape of healthcare has been dramatically transformed by technological advancements, and one of the most promising developments is the use of Virtual Reality (VR) in pain management. This innovative approach is gaining traction as a complementary method to traditional pain relief techniques, offering a novel, non-pharmacological option for patients suffering from chronic and acute pain. This article explores the rise of VR pain management, its mechanisms, applications, benefits, and future prospects.
Understanding VR Pain Management
Virtual Reality (VR) is a computer-generated simulation of a three-dimensional environment that can be interacted with in a seemingly real or physical way by a person using special electronic equipment, such as a headset with a screen inside or gloves fitted with sensors. In the context of pain management, VR immerses patients in a virtual environment that can distract them from their pain, provide relaxation, or even offer therapeutic exercises.
The principle behind VR pain management is rooted in the concept of “distraction therapy.” By engaging multiple senses and capturing the patient’s attention, VR can reduce the perception of pain. This is supported by the gate control theory of pain, which posits that the brain can only process a limited amount of information at a time. When the brain is preoccupied with processing the immersive VR environment, it has less capacity to process pain signals.
Mechanisms of VR Pain Relief
VR pain management works through several mechanisms:
- Distraction: Immersive VR experiences can divert the patient’s attention away from pain. For instance, a patient might be transported to a serene beach or a peaceful forest, providing a mental escape from their physical discomfort.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Some VR programs incorporate elements of CBT, helping patients change their perceptions and responses to pain. These programs might include guided imagery, relaxation techniques, and mindfulness exercises.
- Neuroplasticity: VR can stimulate neuroplasticity, the brain’s ability to reorganize itself by forming new neural connections. This can be particularly beneficial in chronic pain conditions, where the brain’s pain pathways have become maladaptive.
- Biofeedback: Certain VR systems provide real-time feedback on physiological parameters such as heart rate and muscle tension. This can help patients learn to control their body’s responses to pain.

Applications of VR in Pain Management
VR pain management is being applied across a wide range of medical conditions and settings:
- Chronic Pain: Conditions such as fibromyalgia, arthritis, and neuropathic pain can be debilitating. VR offers a non-invasive way to manage these conditions, reducing reliance on medications and their associated side effects.
- Acute Pain: VR has been used effectively in acute pain scenarios, such as post-operative recovery and burn treatment. For example, VR games have been shown to significantly reduce pain perception in burn patients during wound care procedures.
- Pediatric Pain: Children undergoing painful medical procedures or suffering from chronic pain conditions can benefit greatly from VR. The engaging and often playful nature of VR experiences can make medical treatments less intimidating and more tolerable for young patients.
- Rehabilitation: VR is used in physical therapy and rehabilitation to motivate patients and make exercises more enjoyable. This can be particularly useful for patients recovering from surgeries or injuries, where pain can be a barrier to effective rehabilitation.
- Palliative Care: For patients in palliative care, VR can provide comfort and distraction from pain, enhancing their quality of life in their final stages.
Benefits of VR Pain Management
The rise of VR in pain management brings several notable benefits:
- Non-Pharmacological: VR provides a drug-free alternative for pain relief, reducing the risks associated with long-term medication use, such as addiction and side effects.
- Accessibility: As VR technology becomes more affordable and widespread, it has the potential to be accessible to a larger number of patients, including those in remote or underserved areas.
- Personalization: VR programs can be tailored to individual patient needs, preferences, and conditions, offering a personalized approach to pain management.
- Enhanced Compliance: The engaging nature of VR can improve patient compliance with pain management protocols and rehabilitation exercises.
- Holistic Approach: VR can address not only the physical aspects of pain but also the psychological and emotional components, providing a more holistic approach to pain management.
Challenges and Future Prospects
Despite its promising potential, VR pain management faces several challenges:
- Cost and Accessibility: While VR technology is becoming more affordable, the initial investment in hardware and software can still be a barrier for some healthcare providers and patients.
- Technical Issues: VR systems require technical expertise for setup and maintenance, and there can be issues with motion sickness and discomfort for some users.
- Clinical Evidence: While there is a growing body of evidence supporting the efficacy of VR in pain management, more large-scale, long-term studies are needed to establish standardized protocols and best practices.
- Integration into Healthcare Systems: Integrating VR into existing healthcare systems and workflows can be challenging, requiring training for healthcare professionals and adjustments to treatment plans.
Looking ahead, the future of VR pain management is bright. Advances in technology, such as improved graphics, haptic feedback, and artificial intelligence, will enhance the effectiveness and realism of VR experiences. Increased collaboration between technology developers, healthcare providers, and researchers will drive innovation and ensure that VR pain management solutions are evidence-based and patient-centered.
Moreover, as VR becomes more integrated into telehealth platforms, it can offer remote pain management solutions, making it accessible to patients who may not have easy access to specialized pain clinics. This could be particularly valuable in the context of global health crises, such as the COVID-19 pandemic, where remote healthcare solutions are essential.
Conclusion
The rise of VR in pain management represents a significant advancement in the field of healthcare. By offering a non-pharmacological, immersive, and personalized approach to pain relief, VR has the potential to transform the way we manage pain, improving outcomes and quality of life for patients. As technology continues to evolve and more research is conducted, VR pain management is poised to become an integral part of modern medical practice, providing hope and relief to millions of patients worldwide.