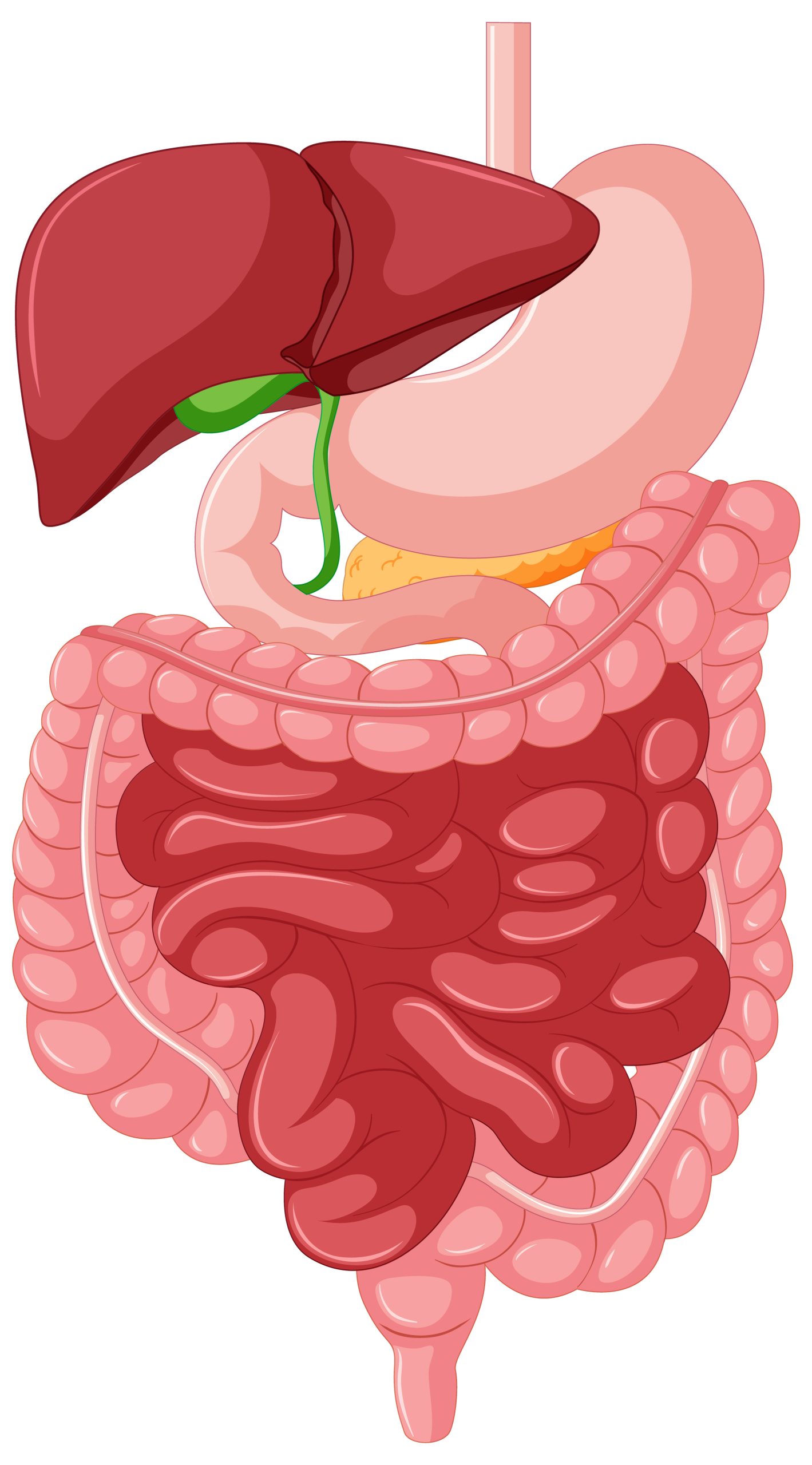
The spleen is a small, fist-shaped organ that plays a crucial role in the body’s immune system. It is located in the upper left side of the abdomen and is responsible for filtering the blood and removing damaged or abnormal cells, such as bacteria and viruses. Despite its importance, the spleen is often overlooked and not fully understood, which can lead to serious health problems. In this article, we will unravel the mysteries of spleen disorders and shed light on this silent sentinel.
Spleen disorders are characterized by a wide range of symptoms, including fatigue, abdominal pain, and anemia. The most common spleen disorders are an enlarged spleen (splenomegaly) and a ruptured spleen (splenic rupture). Splenomegaly can be caused by several factors, including infections, liver disease, and blood disorders. When the spleen becomes enlarged, it can put pressure on surrounding organs, leading to discomfort and pain. In severe cases, splenectomy (spleen removal) may be necessary.
A ruptured spleen, on the other hand, is a medical emergency that requires immediate attention. It can occur as a result of trauma, such as a car accident or a sports injury, or due to an underlying condition, such as infectious mononucleosis. Symptoms of a ruptured spleen include severe abdominal pain, tenderness, and dizziness. Without prompt medical treatment, a ruptured spleen can cause life-threatening internal bleeding.
Another spleen disorder that is less common but equally important is hypersplenism. Hypersplenism is a condition in which the spleen becomes overactive and destroys healthy blood cells, leading to anemia, low platelet counts, and leukopenia (low white blood cell count). Hypersplenism can be caused by a variety of factors, including liver disease, blood disorders, and infections. Treatment options may include medication, blood transfusions, or spleen removal in severe cases.
Diagnosing spleen disorders can be challenging, as the symptoms are often vague and nonspecific. Your doctor may order a series of tests, including blood tests, imaging tests, and a physical exam, to determine the underlying cause of your symptoms. If a spleen disorder is suspected, you may be referred to a specialist, such as a hematologist or gastroenterologist, for further evaluation and treatment.
Managing spleen disorders often involves a combination of medications, lifestyle changes, and in some cases, surgery. For example, if you have an enlarged spleen, your doctor may recommend avoiding contact sports or activities that put you at risk for abdominal injury. In some cases, medication may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and swelling. If your spleen is severely enlarged and causing significant discomfort, spleen removal may be necessary.
Preventing spleen disorders requires maintaining a healthy lifestyle and seeking prompt medical attention for any symptoms or injuries. Avoiding excessive alcohol consumption, maintaining a healthy weight, and getting vaccinated against infections such as pneumococcal disease and influenza can all help protect the spleen and prevent complications.
In conclusion, the spleen is a vital organ that plays a crucial role in the body’s immune system. Spleen disorders can have a wide range of symptoms and can be challenging to diagnose and manage. By understanding the risks and taking steps to protect the spleen, we can help unravel the mysteries of spleen disorders and prevent serious health problems. Remember to seek prompt medical attention for any symptoms or injuries, and work closely with your healthcare provider to manage and prevent spleen disorders.