Introduction:
Pregnancy is a miraculous journey marked by various milestones, with a full-term pregnancy typically lasting around 40 weeks. However, sometimes, this journey takes an unexpected turn with the occurrence of preterm labor and premature birth. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the definitions, symptoms, risk factors, and preventive measures associated with these early occurrences.
What is Preterm Labor and Premature Birth?
The terms “preterm” and “premature” both signify one thing – early. Preterm labor refers to the onset of labor before the completion of 37 weeks of pregnancy. Labor is the natural process through which the body brings a baby into the world. Unfortunately, preterm labor can culminate in premature birth, where the baby is delivered before completing the crucial 40 weeks of gestation required for optimal growth and development within the womb.

Signs and Symptoms of Preterm Labor:
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of preterm labor is crucial for expectant mothers. Here are the key indicators:
- Change in Vaginal Discharge:
- Watery, mucus, or bloody discharge.
- An increase in the amount of vaginal discharge compared to usual.
- Pelvic or Lower Belly Pressure:
- Sensation of pressure in the pelvis or lower abdomen, as if the baby is pushing down.
- Low, Dull Backache:
- Persistent low backache that may feel dull.
- Belly Cramps with or without Diarrhea:
- Abdominal cramps accompanied by or without diarrhea.
- Contractions:
- Regular or frequent contractions causing the belly to tighten like a fist. Contractions may or may not be painful.
- Water Breaking:
- Rupture of the amniotic sac, commonly referred to as the water breaking.
If an expectant mother experiences any of these symptoms, it is imperative to seek prompt medical attention. Timely intervention can make a significant difference in managing preterm labor and potentially preventing premature birth.
Diagnostic Procedures:
When signs of preterm labor are observed, healthcare providers employ various diagnostic procedures to assess the situation:
- Pelvic Exam:
- A pelvic exam may be conducted to determine if the cervix has started thinning out and opening for labor.
- Transvaginal Ultrasound:
- This imaging procedure is performed in the vagina and provides a detailed view of the cervix. It aids in assessing the risk of preterm labor.
- Contractions Monitoring:
- If contractions are present, monitoring their strength and frequency is crucial for evaluating the severity of the situation.
- Additional Tests:
- Depending on the circumstances, additional tests may be conducted to ascertain the presence of preterm labor.
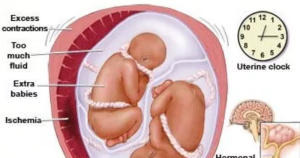
Risk Factors for Preterm Labor and Premature Birth:
Understanding the risk factors associated with preterm labor and premature birth is essential for expectant mothers. While not exhaustive, here are several key risk factors:
- Previous Premature Birth:
- Having a history of delivering a baby prematurely increases the likelihood of experiencing preterm labor again.
- Carrying Multiples:
- Pregnancies involving twins, triplets, or more elevate the risk of preterm labor.
- Uterine/Cervical Issues:
- Problems with the uterus or cervix, whether current or historical, can contribute to the risk of preterm labor.
- Medical Risk Factors Before Pregnancy:
- Being underweight or overweight.
- Family history of premature birth.
- Short interval between pregnancies.
- Medical Risk Factors During Pregnancy:
- Connective tissue disorders (e.g., Ehlers-Danlos syndromes).
- Diabetes.
- High blood pressure and preeclampsia.
- Infections, including sexually transmitted infections.
- Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy (ICP).
- Thrombophilias.
- Risk Factors in Everyday Life:
- Smoking, alcohol consumption, substance abuse.
- High stress levels.
- Low socioeconomic status.
- Domestic violence.
- Prolonged standing or working long hours.
- Exposure to pollutants and chemicals.
- Age and Race:
- Being younger than 17 or older than 35 increases the likelihood of preterm birth.
- Racial disparities, with higher rates observed among black women.

Reducing the Risk:
While some risk factors are beyond control, proactive measures can significantly reduce the risk of preterm labor and premature birth. Here’s a detailed guide on risk reduction:
- Maintain a Healthy Weight:
- Achieve a healthy weight before pregnancy and gain the appropriate amount during gestation.
- Avoid Harmful Substances:
- Quit smoking, avoid alcohol and street drugs, and seek guidance on prescription drug use.
- Timely Prenatal Care:
- Schedule the first prenatal care checkup as soon as pregnancy is suspected.
- Attend all prenatal care checkups, irrespective of feeling fine.
- Manage Chronic Health Conditions:
- Get treated for chronic conditions like high blood pressure, diabetes, and thyroid issues.
- Infection Prevention:
- Discuss vaccinations with your healthcare provider for protection against infections.
- Practice good hygiene, including handwashing and safe sex.
- Stress Reduction:
- Adopt stress-reducing techniques such as healthy eating, regular exercise, and seeking support from family and friends.
- Optimal Pregnancy Spacing:
- Wait at least 18 months between giving birth and getting pregnant again.
- Use birth control until ready for another pregnancy.
By embracing these measures, expectant mothers can actively contribute to a healthier pregnancy journey, Treatment for other health problems minimizing the risk of preterm labor and premature birth.
Comparative Table:
| Risk Factor | Preterm Labor Risk | Ways to Reduce Risk |
|---|---|---|
| Previous Premature Birth | High | Adequate Pregnancy Spacing, Medical Monitoring |
| Carrying Multiples | High | Prenatal Care, Monitoring, Lifestyle Adjustment |
| Uterine/Cervical Issues | High | Medical Intervention, Prenatal Monitoring |
| Medical Conditions | Variable | Timely Treatment, Prenatal Care |
| Lifestyle Choices | Variable | Smoking Cessation, Substance Avoidance, Stress Management |
| Age (Young or Older) | Variable | Healthy Lifestyle, Prenatal Care |
| Race (Black Women) | Higher | Ongoing Research, Enhanced Support |
This extensive guide aims to provide expectant mothers with a thorough understanding of preterm labor and premature birth, empowering them to make informed decisions for a healthier and safer pregnancy journey.
Conclusion:
The journey of pregnancy is a unique and transformative experience, filled with anticipation and joy. However, the potential challenges of preterm labor and premature birth underscore the importance of awareness, timely intervention, and proactive measures. By understanding the signs, risk factors, and preventive strategies outlined in this guide, expectant mothers can navigate their pregnancy journey with informed choices, ensuring the best possible outcome for both themselves and their precious newborns.




