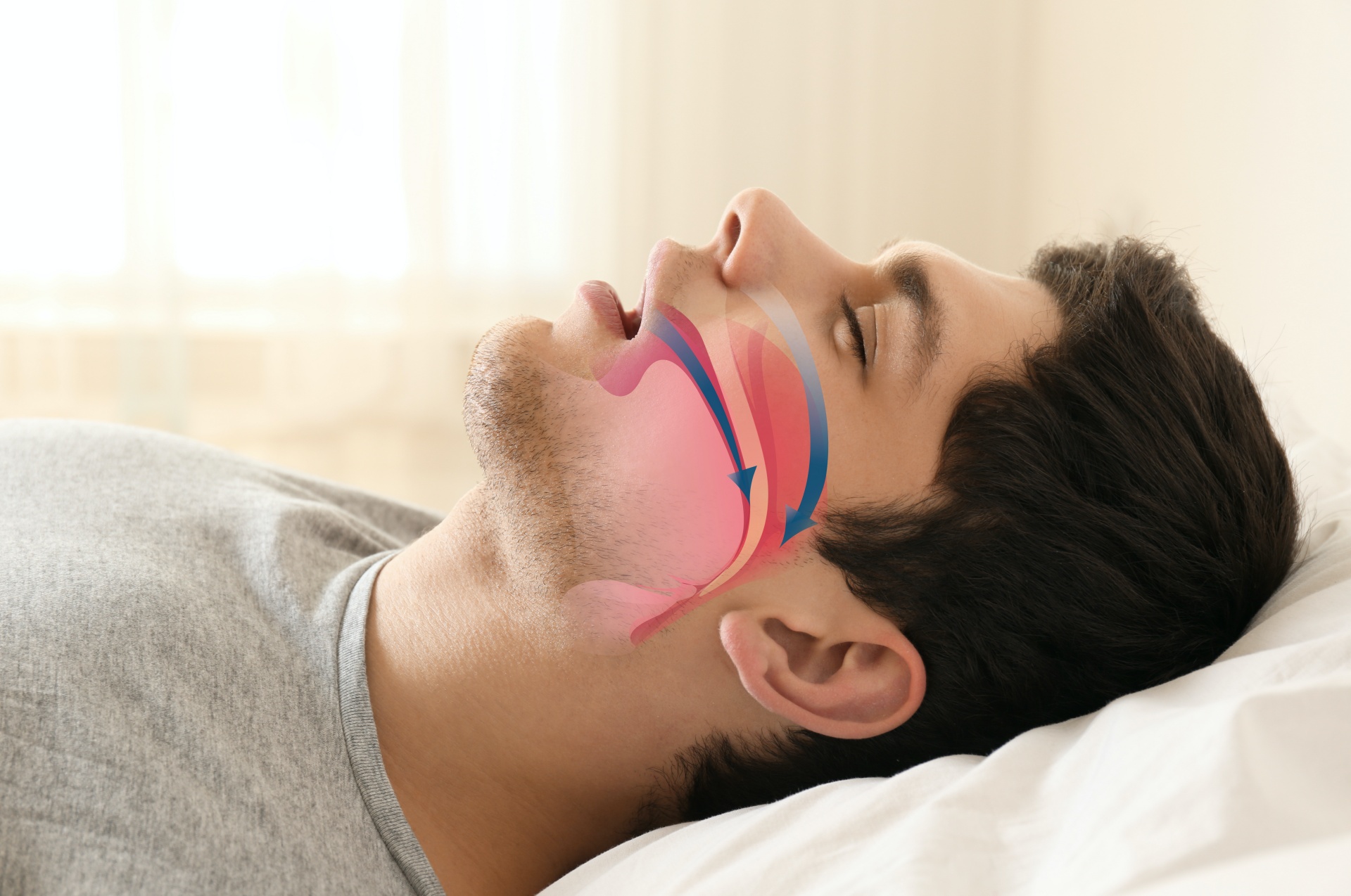
Introduction
Sleep apnea is a prevalent sleep disorder characterized by interruptions in breathing during sleep. While it’s commonly associated with symptoms like daytime fatigue and snoring, many are unaware of its potential impact on dental and skeletal health. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricate relationship between sleep apnea and its adverse effects on bones and teeth. Explore More About (Kidney Health Food And Veggies)
The Link Between Sleep Apnea and Dental Health
Dental Problems Associated with Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea can significantly affect oral health, leading to various dental issues such as:
- Bruxism: Individuals with sleep apnea are more prone to bruxism, a condition characterized by teeth grinding or clenching during sleep. This can result in tooth wear, fractures, and even tooth loss over time.
- Dry Mouth: Reduced saliva flow is common among sleep apnea sufferers due to mouth breathing and snoring. Saliva plays a crucial role in protecting teeth against decay and maintaining oral hygiene. Dry mouth increases the risk of cavities, gum disease, and oral infections.
- Periodontal Disease: The prevalence of periodontal (gum) disease is higher in individuals with sleep apnea. Untreated periodontal disease can lead to gum recession, tooth mobility, and eventual tooth loss.
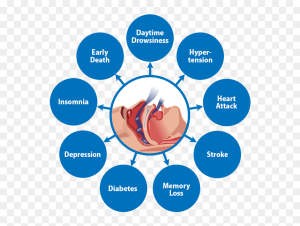
Impact of Dental Health on Overall Well-being
Maintaining good dental health is essential not only for a healthy smile but also for overall well-being. Poor oral health has been linked to various systemic conditions, including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and respiratory infections. Addressing dental issues associated with sleep apnea is crucial for mitigating these risks and improving quality of life.
Sleep Apnea and Bone Health
Effects of Sleep Apnea on Bone Density
Emerging research suggests a correlation between sleep apnea and decreased bone density. Chronic sleep deprivation and intermittent hypoxia associated with sleep apnea can disrupt the body’s bone metabolism, leading to bone loss and increased fracture risk.
Hormonal Imbalance and Bone Health
Sleep apnea can also disrupt hormonal balance, particularly affecting hormones crucial for bone health, such as growth hormone and cortisol. These hormonal imbalances contribute to accelerated bone resorption, further exacerbating bone loss and weakening skeletal integrity.
Association with Osteoporosis
Studies have indicated a potential association between sleep apnea and osteoporosis, a condition characterized by fragile and brittle bones. Individuals with sleep apnea may be at a higher risk of developing osteoporosis due to the cumulative effects of sleep disturbances on bone health.
Managing Sleep Apnea to Preserve Dental and Skeletal Health
Lifestyle Modifications
- Weight Management: Obesity is a significant risk factor for sleep apnea. Losing excess weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise can help alleviate symptoms and improve overall health, including dental and skeletal wellness.
- Sleep Hygiene: Practicing good sleep hygiene habits, such as maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, creating a conducive sleep environment, and avoiding stimulants before bedtime, can enhance sleep quality and reduce the severity of sleep apnea.
Oral Appliance Therapy
For individuals with mild to moderate sleep apnea, oral appliance therapy may be recommended as a non-invasive treatment option. Custom-fitted dental devices, such as mandibular advancement devices, help keep the airway open during sleep, reducing snoring and episodes of apnea.
Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP)
CPAP therapy is the gold standard treatment for moderate to severe sleep apnea. It involves wearing a mask connected to a machine that delivers a continuous flow of air to keep the airway open during sleep. CPAP effectively alleviates symptoms, improves sleep quality, and reduces the risk of complications associated with untreated sleep apnea.
Oral Health vs. Skeletal Health in Sleep Apnea
| Aspect | Oral Health | Skeletal Health |
|---|---|---|
| Dental Problems | Bruxism, dry mouth, periodontal disease | Decreased bone density, bone loss, increased fracture risk |
| Impact on Overall | Linked to cardiovascular disease, diabetes, respiratory infections | Associated with osteoporosis, hormonal imbalances, bone resorption |
| Management | Lifestyle modifications, oral appliance therapy, CPAP | Weight management, sleep hygiene, CPAP therapy |
Conclusion
Sleep apnea extends its detrimental effects beyond mere sleep disturbances, significantly impacting dental and skeletal health. By addressing dental and skeletal issues associated with sleep apnea through lifestyle modifications and appropriate treatments such as oral appliance therapy and CPAP, individuals can mitigate risks and improve overall well-being. Prioritizing sleep health is essential for breaking free from the detrimental cycle of sleep apnea and enjoying a healthier, more vibrant life.
For more information and expert guidance on managing sleep apnea and its effects on dental and skeletal health, consult with a qualified healthcare professional.




